As a student, the prospect of studying O Level & IGCSE Accounting may initially appear pointless and even tedious. The question often arises: what practical use could learning about basic accounting concepts offer? However, accounting holds significant relevance, serving as the backbone for numerous organizations today. Whether in a corporate setting or a non-profit entity, accounting plays a crucial role in establishing the foundation for successful operations.
In this article, we will talk about some of the most basic accounting concepts and explore the role these O Level & IGCSE Accounting concepts play in business operations.
Basic Accounting Concepts – What Are They?
Every financial or business institution needs basic accounting concepts to do everyday tasks such as recording financial dealings and maintaining bookkeeping. Not only does this help corporations interpret financial transactions, but it also ensures transparency and cost efficiency.
Financial managers and accountants use basic accounting concepts in financial reports such as income statements, balance sheets, etc. These documents are based on 11 main accounting principles upon which various organizations – sole proprietorships, partnerships or public and private companies – base all their financial transactions. Let’s take a look at them now.
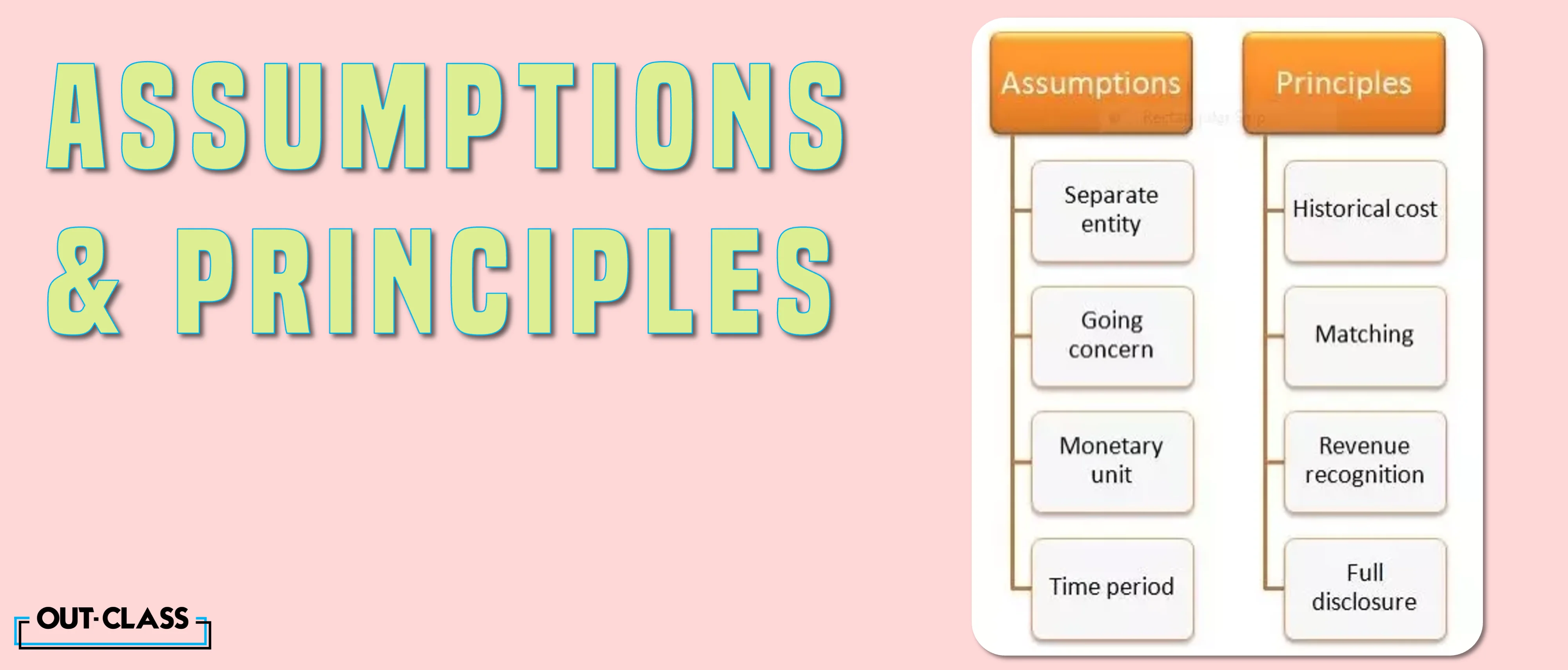
Basic Accounting Concepts Principles and Guidelines:
There are about 11 basic accounting concept principles and guidelines. Let's delve deeper into what they are:
1. Business Entity Concept
The business entity concept, also known as the ‘economic entity’ or ‘separate entity’ concept, assumes that the organization and its owner are two separate identities.
This means that an organization may not record its owner’s personal information such as their personal expenses, income, liabilities and assets as part of the business.
Benefits:
-
ensures clarity: especially when it comes to keeping track of the business’s own income and expenses along with its tax deductions.
-
protects the business owner’s own personal finances: and helps them maintain their credit rating.
-
allows the organization's stakeholders to make important business decisions based on the company’s performance, not on the owner’s financial standing.
2. Going Concern Concept
This concept is based on the assumption that the business will continue for many years to come or, at least, for the foreseeable future, i.e. for 12 months from the date of reporting. With this assumption, the owner can continue to keep a record of all financial transactions, develop income statements and balance sheets, maintain bookkeeping, etc.
Important Tip:
A business cannot apply the going concern concept if it is:
-
unable to pay dividends
-
unable to raise credit from banks and other financial services
-
is incurring losses
-
experiencing a negative cash flow
-
unable to pay off debts
-
facing a lawsuit then they.
3. Money Measurement Concept
This one may seem a little bit on the nose, however, it is still important. This concept is based upon the assumption that businesses and corporations can only record transactions that can be measured or quantified in terms of money.
Anything that does not hold any monetary value is not recorded in any financial statement or transaction.
This even holds for non-monetary items such as employee competence, product quality, market sentiment, etc. While they may have a significant bearing on the performance of the corporation, such non-monetary items cannot be placed in financial reports or statements as quantifying them would be challenging.
4. Accounting Period Concept
This concept describes the typical timeframe within which a business is meant to prepare financial statements or a record of all its financial transactions for the sake of its internal and external stakeholders. For an internal finances review, the time is either three to six months or every month, depending on how often a corporation wishes to assess its cash flows. For external stakeholders, such as for the government and company investors, that period is up to a year.
5. Accrual Concept
Another basic accounting concept involves the accrual concept. This states that a business must record a financial transaction as and when it occurs, regardless of whether payment is made at that time or a later date. This enables organizations to record and ultimately report on important financial information, such as income, assets, expenses, liabilities, etc. accurately.
6. Revenue Realization Concept
Similar to the accrual concept, the revenue realization concept (also known as the ‘revenue recognition’ concept) states that the company must record the potential revenue expected to be earned from the transaction. While ownership may have been transferred from seller to buyer, the way it will be recorded will be creating a receivable against the buyer’s name in their records. Another entry is created to record the owed amount that is then received.
7. Full Disclosure Concept
This requires an organization to fully disclose or show its financial statements and reports to relevant stakeholders such as potential investors or the government (for tax and auditing purposes) as well as creditors, shareholders, clients, etc. It includes revenue recognition, depreciation, inventory, taxes, earnings, stock value, leases and liabilities.
8. Dual Aspect Concept
This concept states that every financial transaction affects two accounts of a business. Meaning, that every transaction involves a giver and a receiver or, in this case, a debit and a credit. Maintaining this principle or assumption ensures clarity and accuracy in accounting which is why it is considered a standard in bookkeeping.
9. Materiality Concept
This includes guidelines that help identify whether a piece of financial information should be considered material or not, i.e. if it has the potential to impact the opinion of the person viewing the financial statements. In such cases, the business may decide to remove certain transactions that may have no financial bearing upon its final accounts. Of course, this differs from company to company; for example, a larger company may be more open towards removing various financial transactions as compared to smaller companies.
10. Verifiable Objective Evidence Concept
This one is a bit of a no-brainer and is naturally one of the cornerstones of accounting; the ability of a business to produce verifiable documentation of each of their financial transactions. Otherwise, such transactions will be considered biased or unreliable and may potentially cause further irregularities within an organization’s finances.
11. Historical Cost Concept
Lastly, this concept talks about the importance of recording the value of assets owned by a company at their historical cost, i.e. the cost at which they were bought, rather than their current market value. This ensures consistency along with reliability as the alternative would involve having to change their valuation every few weeks or months.
Conclusion
Being able to understand these concepts is essential for anyone looking to build a career in accounting as this helps accountants accurately record, analyze and interpret financial information. If you are interested in learning more about accounting, head on over to www.out-class.org and sign up for our O Level/IGCSE Accounting course!