Darcy’s law can be a confusing concept to grasp in Physics. This brief guide states Darcy’s law with examples to help you with a concise explanation!
#1: What is Darcy’s Law?
Darcy’s law is a concept from fluid mechanics and is often used to explain groundwater flow. Simply, it models the flow of a fluid (like water) through a porous medium (like gravel or soil).
#2: Darcy’s law equation
Darcy’s law equation is:
Q = -kAPL
Where:
-
Q is the volumetric flow rate (volume of fluid passing per unit of time).
-
k is the intrinsic conductivity of the porous medium. It represents how easy or difficult it is for the fluid to pass through the given medium
-
A is the cross-sectional area perpendicular to the flow direction.
-
P is the change in water pressure in the direction of flow.
-
L is the length of the water column being considered.
#3: Darcy’s law derivation
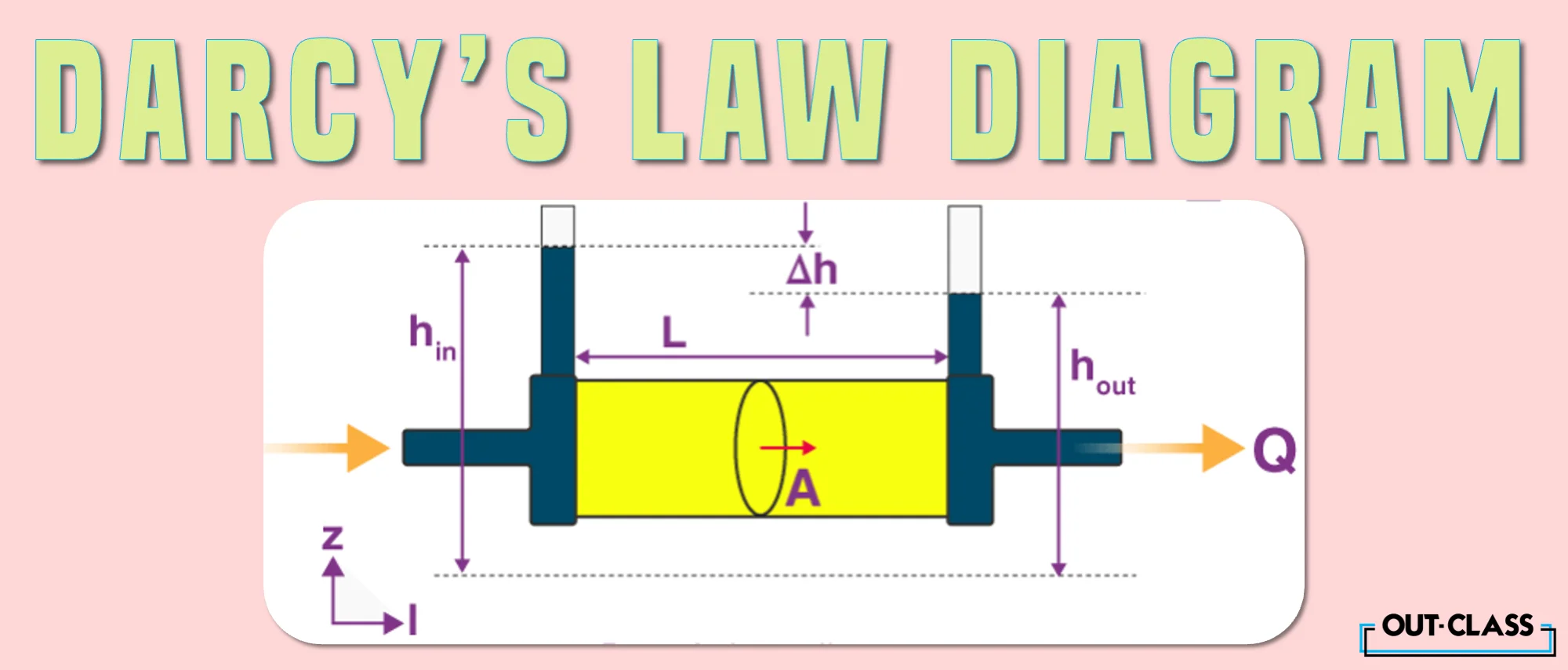
Darcy’s law equation examples are numerous and can help understand the derivation. One such example is given below:
Imagine a column of water-filled soil of area A, with a height L. Between the top and bottom, there is a water pressure difference P. The difference in pressure over the height causes water flow. Hence, the greater the fraction PL, the greater the flow of water.
Also, if we increase the cross-sectional area A, more water can flow. Hence, Q is proportional to the A and PL. The relation is linked by a given medium's permeability/conductivity k (like soil). Hence, we get: Q = -kAPL
#4: Limitations of Darcy’s law:
Unfortunately, Darcy’s law equation assumes ideal scenarios (laminar flow) that don’t always occur in the real world. Therefore, it cannot model groundwater flow accurately where there are large pores in the medium creating turbulent flow.
FAQs:
Q. What is the significance of Darcy’s law in fluid mechanics?
Darcy’s law is essential in fluid mechanics, particularly for modeling the flow of fluids through porous mediums. It provides a fundamental understanding of groundwater flow and permeability.
Q. How is Darcy’s law applied in real-world scenarios?
Darcy’s law is applied to scenarios involving fluid flow through porous materials, such as soil or gravel. It is frequently used in hydrogeology to model groundwater movement.
Q. What does the negative sign in Darcy’s law equation signify?
The negative sign indicates that the flow is in the direction of decreasing hydraulic head or pressure.
Q. Can Darcy’s law accurately model turbulent flow in real-world conditions?
No, Darcy’s law assumes ideal scenarios with laminar flow. It may not accurately model turbulent flow situations, especially in scenarios with large pores in the medium.