If you wish to understand the origins of life, then the study of atoms and molecules becomes essential as they form the very building blocks of all matter on Earth. Everything you can see, touch, smell or taste and every living being (including you and everyone you have ever met) is made up of atoms and molecules.
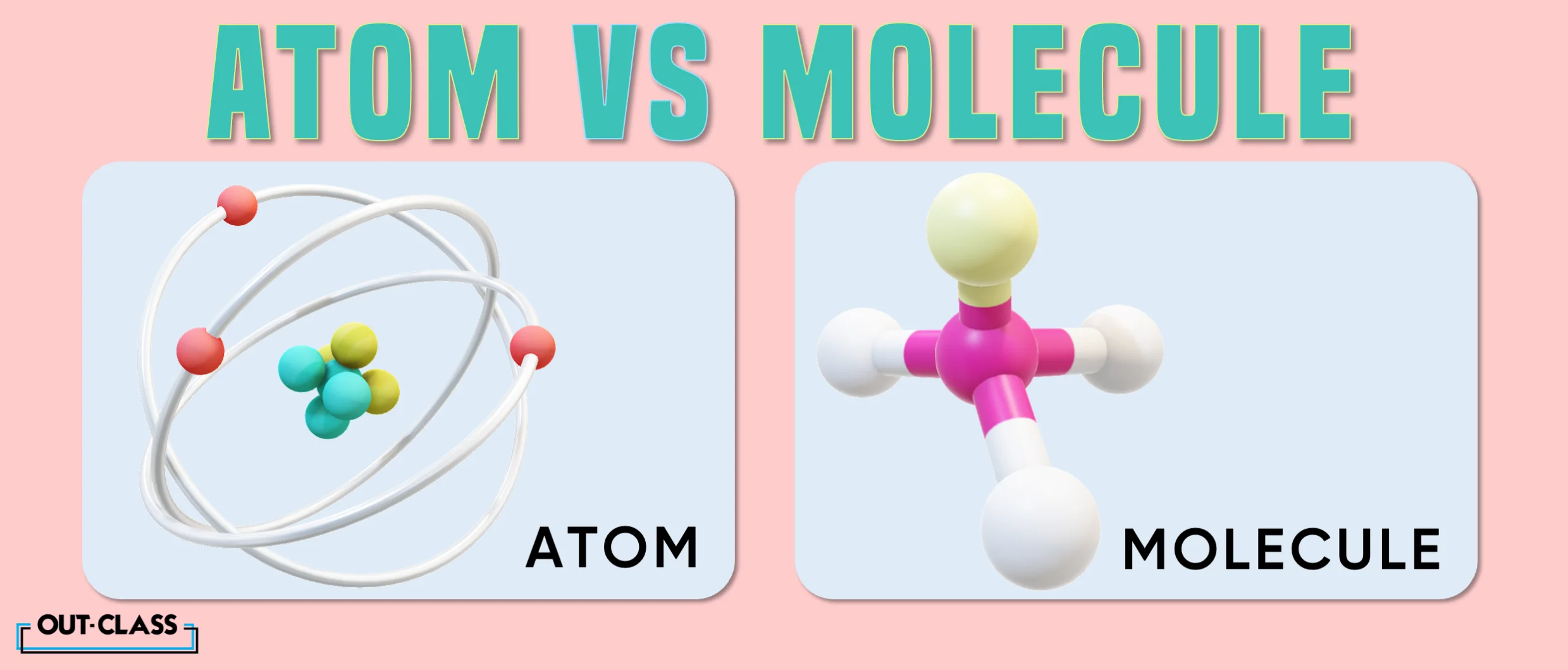
Multiple similarities exist between these microscopic entities (i.e. they make up the main components of both living and non-living matter, etc.), but the fact of the matter (pun intended) is that atoms and molecules are quite different from each other.
How are Atoms Different from Molecules
Are Molecules Made Up of Atoms?
An atom is the smallest unit in the universe. Some cells, such as plant and animal cells, are made up of atoms. Molecules, on the other hand, are made up of one or two or more atoms. An example is water, which has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
The Missing Link Between Atoms and Molecules
One distinct feature of atoms is that they can exist independently of molecules and other elements of matter whereas molecules cannot exist without atoms.
Stability Vs Instability
Another difference is that an atom may not always be stable due to the presence of electrons in its outer shells (as electrons always contain a positive charge). Molecules are, in contrast, formed to attain stability.
Reactive Charge
Finally, except for noble elements, atoms of all other elements contain a certain level of reactive charge. In contrast, molecules have a relatively lower level of reactivity, mainly because they are made up of different elements that ensure some valence points (i.e. the combining capacity of an atom of a given element, determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with) are filled up by available electrons.
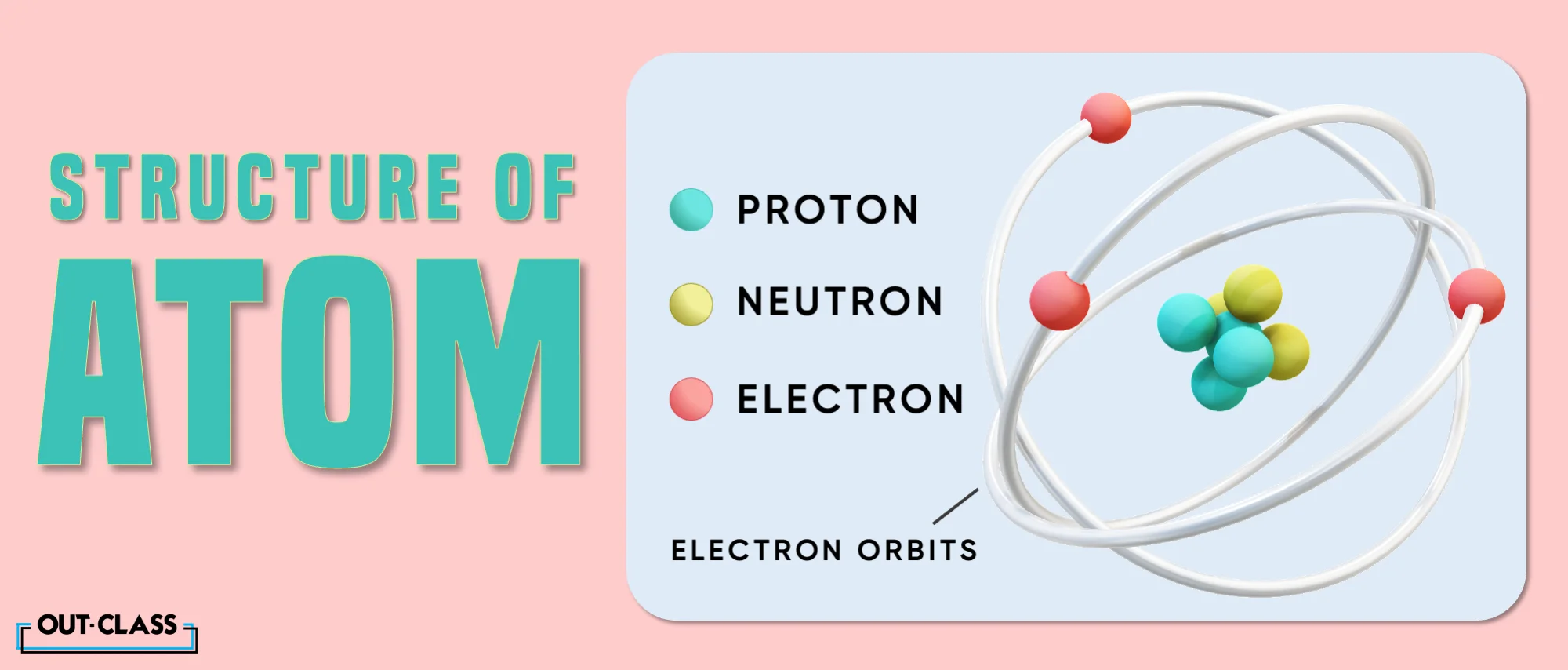
What is an Atom?
As explained above, an atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. Each atom is made up of neutrons, protons and electrons. The neutrons (which have a neutral charge) and the protons (which have a positive charge) form the central nucleus within an atom that is further surrounded by electrons (which have a negative charge). Each of these elements can coexist due to a balance in electrical charge.
Not all atoms are the same. Each atom is made up of a different number of protons, thereby leading to each being distinguishable by its own atomic number or atomic mass (i.e. the total number of protons and neutrons). In addition, no atom is visible to the naked eye; optical tools such as the electron microscope are needed to study them. They are also indivisible, i.e. they cannot be divided except through nuclear fission (I’m looking at you, Oppenheimer).
All atom-related knowledge comes from the study of atomic theory, a concept created by the Greek sage, Democritus in around 400 BCE.
What is a Molecule?
The concept of a molecule is a theory brought about by Italian chemist, Avogadro (between 1776 and 1856), while he was working on determining the volume of gases. His theory stated that the discrepancy in volumes was because some gases exist as diatomic molecules i.e. they are made up of two atoms.
The Relationship between Atom and Molecule
Molecules can be made up of the same or different elements. Some may have few bonded atoms, others may contain a large number of them and, unlike atoms, they can come in different shapes and sizes.
Other Features of Molecules:
Other features about molecules are that they are divisible and that they can create interactions between them. This is due to ionic or covalent bonds.
-
Ionic bonds are established when an electrical charge is made due to a charge difference between atoms (i.e. when an electron is transferred to another, thus forming a bond).
-
A covalent bond is formed when an electron is shared between two atoms.
These prevent the molecules from having any charge whatsoever, thus making them electrically neutral.