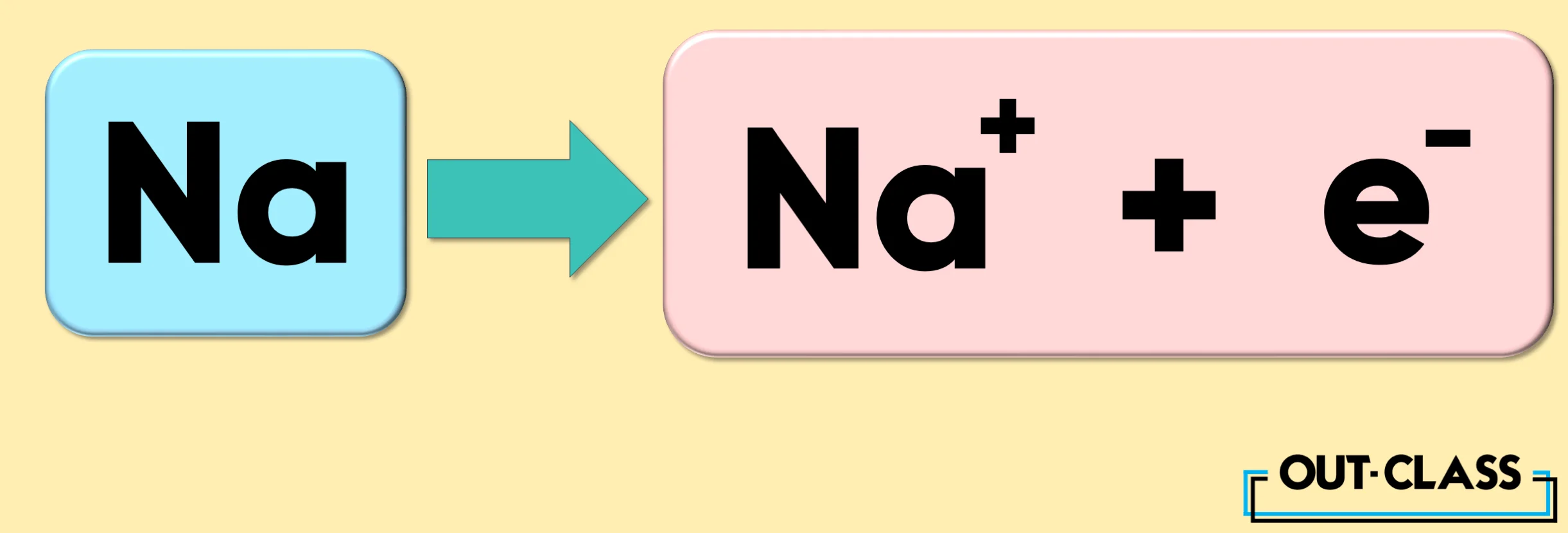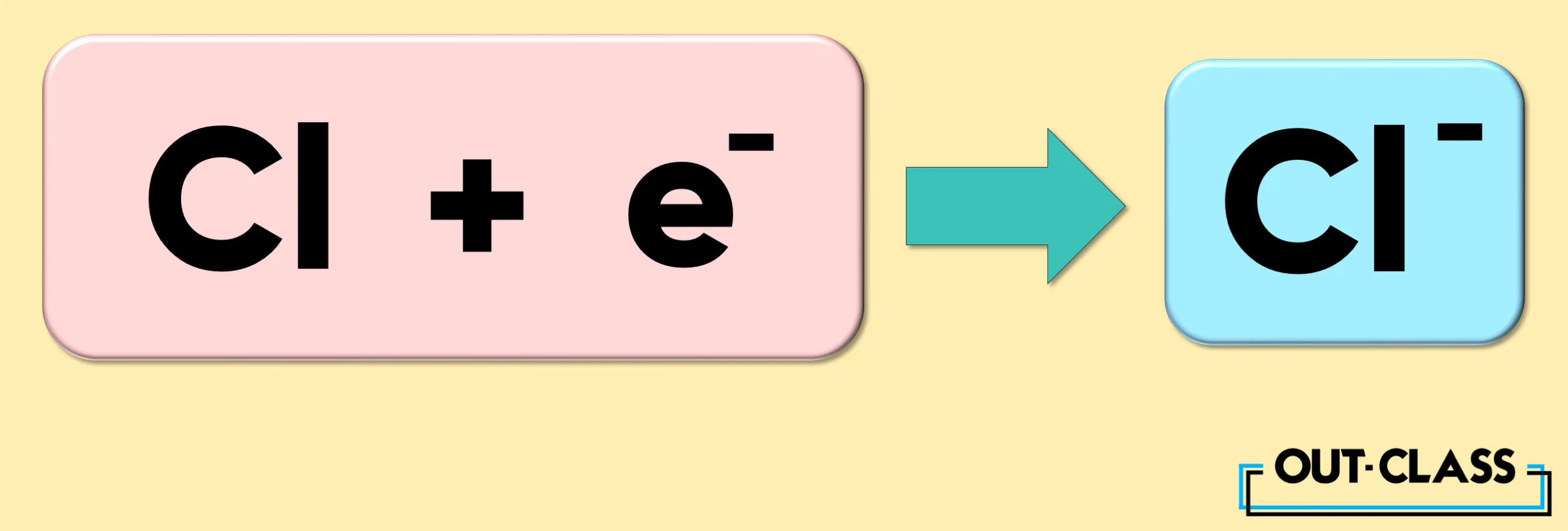"Cations Vs. Anions? Ionic compounds? Difference between cations and anions?" You're in your IGCSE/O Level Chemistry class, and these questions start popping up in your head.
As your teacher talks about the chemical significance of cations and anions, you’re amused but wait….. do you understand the difference between them?
Don’t worry. We’re here for you.
By the end of this blog, you'll be able to confidently explain the difference between cations and anions to your friends and maybe flex your Chemistry knowledge in class for once. 😉
What are Cations and Anions?
Now, let's dive straight into the definitions of cations and anions.
What are cations?
Cations are positively charged ions that have lost one or more electrons.
What are anions?
Anions are negatively charged ions that have gained one or more electrons. Now, what on earth is an “ion”?
What is an Ion?
An ion is any atom or molecule that carries a positive (+) or negative (-) charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. Cat-ions are, therefore, positive (+) ions and an-ions are negative (-) ions.
Take the element Sodium (Na), for example. When it loses an electron, it becomes a cation with a charge of +1.
Related: How to Calculate a Charge on an Ion?
On the other hand, the element Chlorine (Cl) gains an electron to become an anion with a charge of -1.
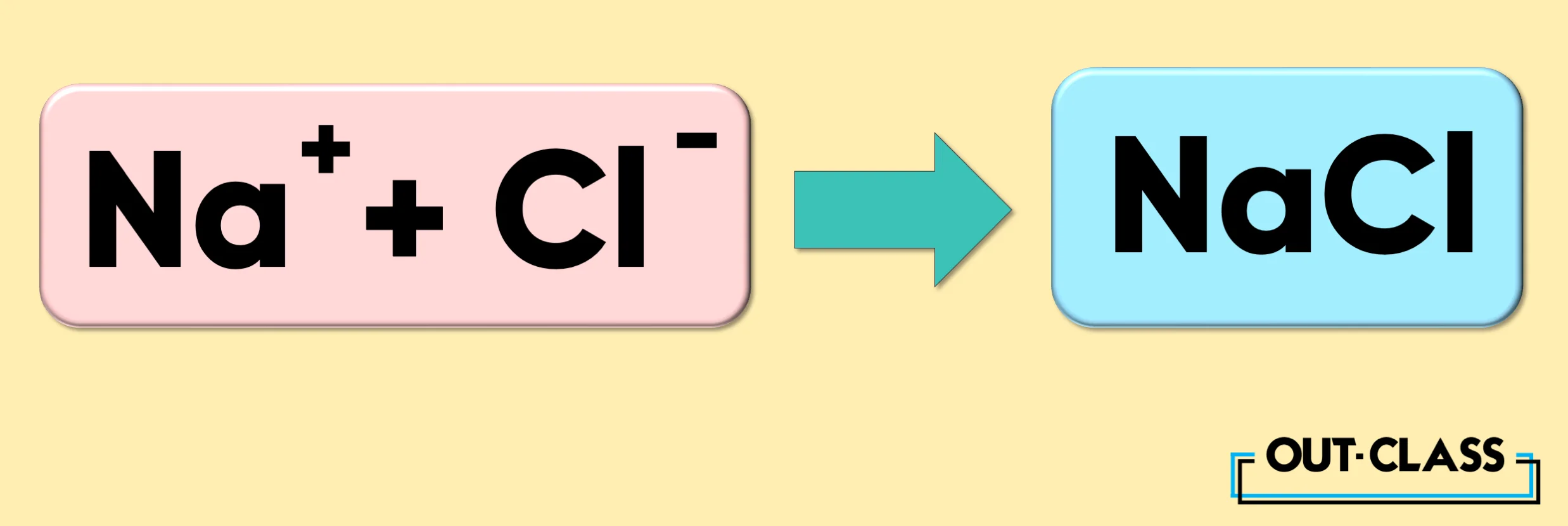
When cation Na+ and anion Cl- come together, they form an ionic compound essential to human existence; they form table salt (NaCl)!
What is the Difference Between a Cation and Anion?
The main difference between cations and anions is their charge. Cations have a positive charge, while anions have a negative charge. Additionally, cations are smaller in size compared to anions, which is why they behave differently in chemical reactions.
This is because when cations lose electrons from their outermost shells, the positive charge of the protons in the nucleus has a stronger "hold" on the remaining electrons as there are fewer electrons in the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus to repel the positive (effective) nucleus charge.
The same principle applies in reverse on anions.
Is Mg2+ a Cation or Anion?
Now, let's put our knowledge to the test. Is Mg2+ a cation or anion? If you said cation, you're absolutely right! Magnesium (Mg) has two valence electrons, and when it loses them, it becomes a positively charged ion (Mg2+).
I hope you've enjoyed learning about the difference between cations and anions. Just like how cricket teams need the efforts of both bowlers and batters to win a match, ionic reactions also need a balance of cations and anions to form an ionic compound successfully.
Keep exploring and learning Chemistry, and before you know it, you'll be ready to ace your exams and impress your peers with your knowledge! 🤩
FAQs:
Q. What is the difference between cations and anions?
The main difference lies in their charge. Cations are positively charged ions formed by the loss of one or more electrons, while anions are negatively charged ions formed by gaining one or more electrons.
Q. Can you provide examples of cations and anions?
Certainly! An example of a cation is Na+ (Sodium ion), formed by the loss of an electron. An example of an anion is Cl- (Chloride ion), formed by gaining an electron.
Q. How do cations and anions come together to form ionic compounds?
When cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions) come together, they form ionic compounds. For example, the combination of Na+ (cation) and Cl- (anion) forms table salt (NaCl).
Q. Is there a size difference between cations and anions?
Yes, there is a size difference. Cations are smaller in size compared to anions. This size difference affects their behavior in chemical reactions.
Q. Why do cations have a stronger "hold" on electrons compared to anions?
When cations lose electrons from their outermost shells, the positive charge of the protons in the nucleus has a stronger "hold" on the remaining electrons. There are fewer electrons in the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus, leading to a stronger attraction.
Q. How do cations and anions contribute to ionic reactions?
Ionic reactions require a balance of cations and anions to form an ionic compound successfully. The combination of positively and negatively charged ions results in the formation of stable compounds.