Have you ever wondered what makes a fan spin, a wheel roll, or even a planet orbit? I’m sure you have. Well, not to get too sciency, but these are all examples of different types of IGCSE and O Level Physics motion that involve rotation.
But what exactly is rotation, and how does it differ from circular motion?
You’ve come to the right place! In this article, we will explore the IGCSE and O Level Physics concepts of rotatory and circular motion.
What is Rotatory Motion?
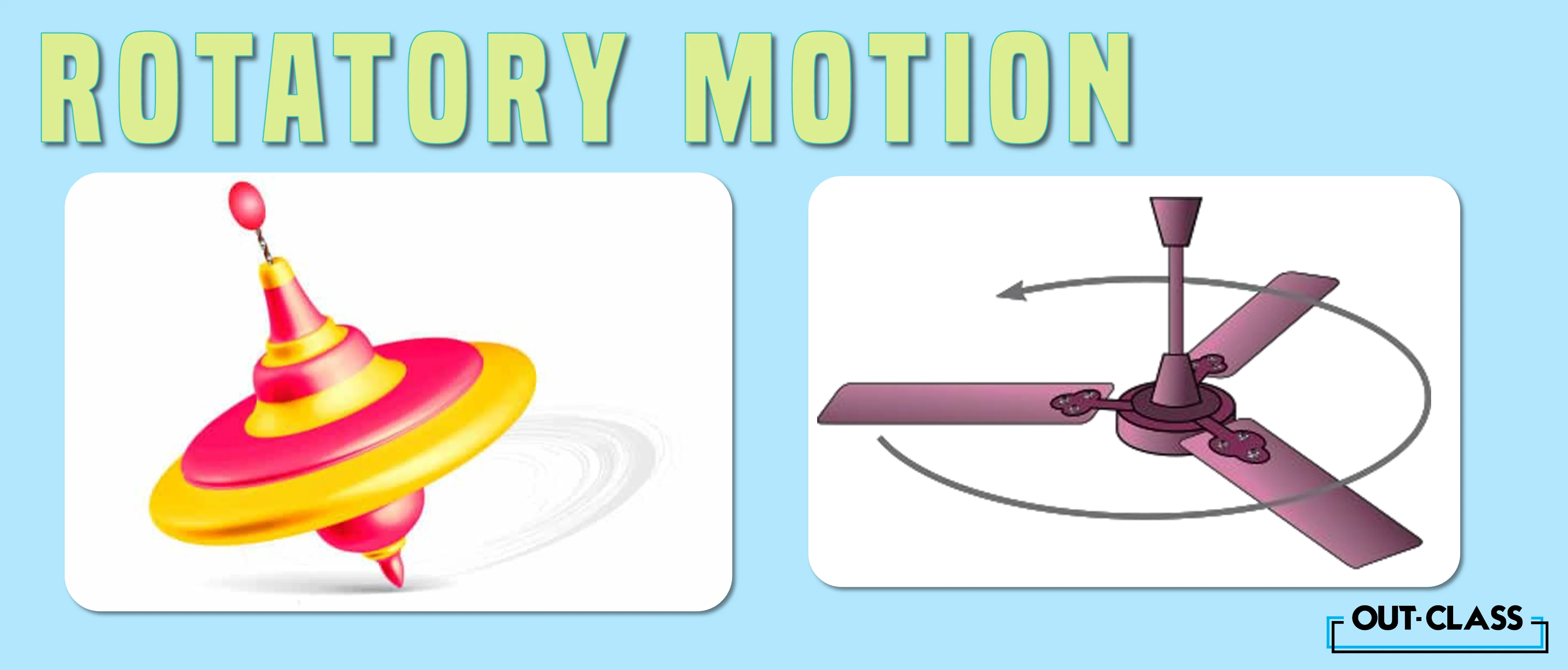
Simply put, rotatory motion is the motion of a body that spins or rotates about an axis. The axis of rotation can be inside or outside the body, and this axis can be fixed or constantly changing. For example, a spinning top has a rotatory motion about an axis which passes through its centre and remains fixed. However, a helicopter has a rotatory motion about an axis that passes through its rotor blades and is changing.
What is Circular Motion?
Well, circular motion is a special case of rotatory motion. Here, the body moves in a circle around a fixed axis outside the body.
*Note: The distance between the centre of body mass and the rotation axis remains constant.
For example, a ball tied to a string and swung around has a circular motion. This example shows an axis that passes through the centre of the string and remains fixed. A satellite orbiting the Earth has a circular motion about an axis that passes through the Earth's centre and remains fixed.
The Main Difference Between Circular and Rotational Motion:
To answer your question, the main difference between rotational and circular motion is that in rotatory motion, the body can have any shape and size, and the axis of rotation can be anywhere and can change. In circular motion, however, the body is treated as a point mass, and the axis of rotation remains fixed and outside the body.
Circular and Rotatory Motion Examples:
Examples of Rotatory Motion
Here are 5 examples of rotatory motion:
-
A spinning fan about its hub.
-
A rolling wheel about its axle.
-
A drilling machine rotating about its bit.
-
A potter's wheel spinning about its center.
-
A tornado swirling about its core.
Examples of Circular Motion
Here are 5 examples of circular motion:
-
A swinging ball around a pole.
-
A car turning around a curve.
-
A Ferris wheel rotating about its centre.
-
A clock's hands moving around its face.
-
A merry-go-round spinning about its centre.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rotatory motion is the spinning or rotating of a body around an axis, with the axis's position and shape being flexible. A particular kind of rotatory motion known as circular motion happens when a body moves in a circle around a stationary external axis, treating the body as a point mass.
The primary distinction between circular and rotatory motion is that the former treats the body as a point mass with a fixed external axis, and the latter treats the body's flexibility and axis variability. Examples illustrate the various ways in which these IGCSE & O Level Physics motions appear in our everyday lives. Examples include rolling wheels, spinning fans, and swinging balls. Understanding these IGCSE and O Level Physics concepts helps us better appreciate how rotatory and circular motion interact to shape our environment.
FAQs:
Q. What is Rotatory Motion?
Rotatory motion is the movement of an object as it spins or rotates around an axis. This axis can be inside or outside the object and may be fixed or changed.
Q. What is Circular Motion?
Circular motion is a special type of rotatory motion where an object moves in a circle around a fixed axis located outside the body, with the distance from the axis remaining constant.
Q. What is the Difference Between Rotatory and Circular Motion?
The key difference is that in rotatory motion, the object can have any shape, and the axis can change or be inside the object. In contrast, circular motion treats the object as a point mass, with a fixed axis outside the object.
Q. Can You Give Examples of Rotatory Motion?
Yes, examples of rotatory motion include:
- A spinning fan.
- A rolling wheel.
- A drilling machine.
- A potter's wheel.
- A tornado.
Q. What Are Examples of Circular Motion?
Examples of circular motion include:
- A ball swinging around a pole.
- A car turning on a curved path.
- A Ferris wheel.
- A clock’s hands.
- A merry-go-round.
Q. Why is Understanding Rotatory and Circular Motion Important in Physics?
Understanding these concepts helps explain how various objects move in real life, from simple machines like fans and wheels to complex systems like satellites and planets.
Q. How is Circular Motion a Special Case of Rotatory Motion?
Circular motion is a special case of rotatory motion because it involves movement in a perfect circle around a fixed axis, while rotatory motion can involve different shapes and variable axes.
Q. How Does Circular Motion Apply to Satellite Orbits?
Satellites exhibit circular motion as they orbit Earth in a path where the axis of rotation passes through the Earth’s center and remains fixed.
Q. How Do Rotatory and Circular Motions Differ in Axis Location?
In rotatory motion, the axis can be inside or outside and may change, while in circular motion, the axis is always fixed and outside the object.