Studying IGCSE or O Level Chemistry involves exploring the relationship between the different kinds of matter that exist in our physical world. This can further be classified into elements, compounds and mixtures. But how do we tell if a substance is an element, a compound or a mixture?
In this article, we will explore the differences between an element, a compound and a mixture, along with the properties of each.
Element
What is an Element?
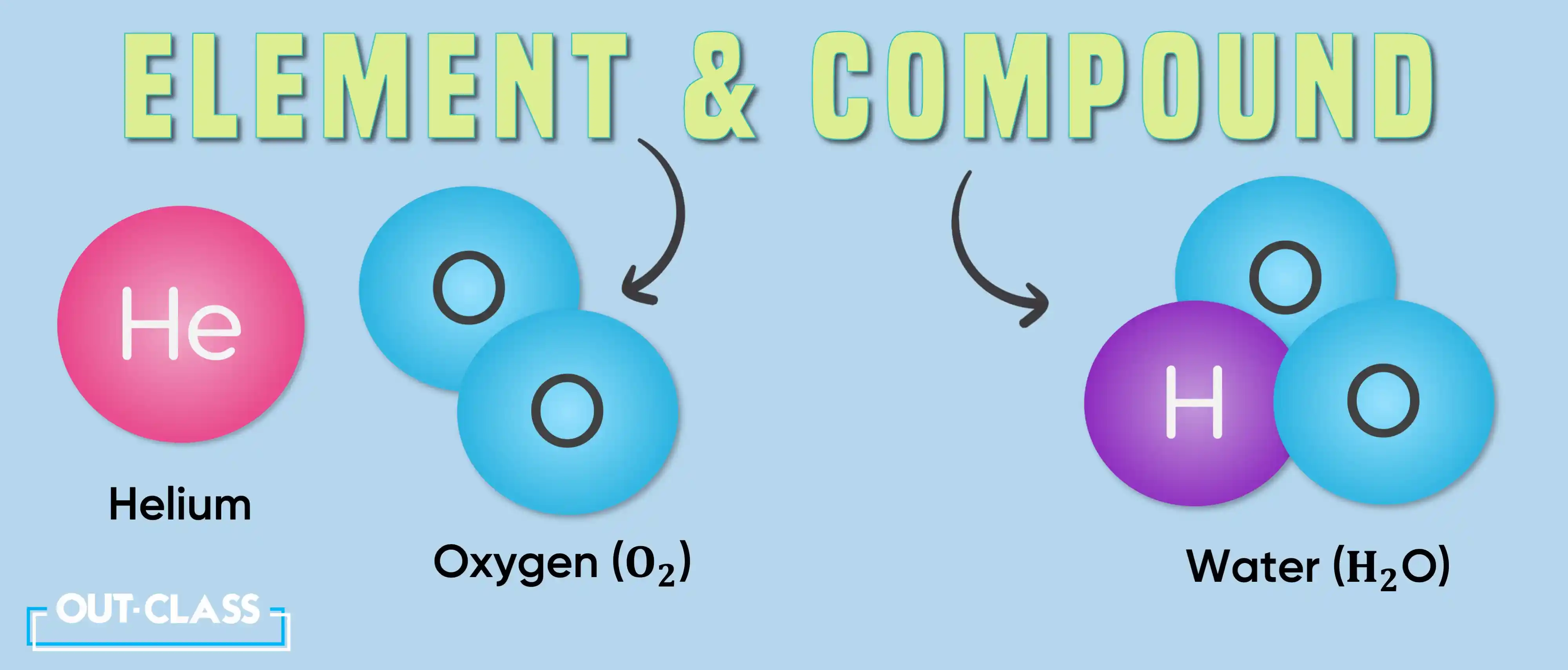
An element can be described as a pure substance which consists of only one type of atom. Hence, it cannot be split into two or more substances through chemical means.
There are generally two forms of elements:
-
State – i.e. solids, liquids and gases
-
Metals – i.e. non-metals and metalloids (which have properties of both metals and non-metals, e.g., silicon and germanium)
Examples of Elements
Elements are usually represented by their chemical names and symbols. Here are 10 examples of elements along with their chemical symbols:
-
Calcium (Ca)
-
Carbon (C)
-
Chlorine (Cl)
-
Hydrogen (H)
-
Oxygen (O)
-
Iron (Fe)
-
Neon (Ne)
-
Silicon (Si)
-
Sodium (Na)
-
Germanium (Ge)
Compound
What is a Compound?
A compound is a substance that is made up of two or more different elements that have been chemically combined in fixed proportions. This means that it can be broken down through chemical processes such as thermal decomposition and electrolysis (the process of using electricity to break up a compound).
Compounds are usually found in two forms:
-
Covalent compounds (which are made up of molecules)
-
Ionic compounds (which are made up of ions)
Related: Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Examples of a Compound
Compounds can be identified with the help of a chemical name that indicates the types of elements present within. These include:
-
Sodium chloride or common salt (which contains sodium and chlorine)
-
Carbon dioxide (which contains carbon and oxygen)
-
Copper II sulfate (which contains copper, sulfur and oxygen)
-
Magnesium oxide (which contains magnesium and oxygen)
Another way that compounds can be represented is through chemical formulae. This can be done by putting the formula of the elements that make up the compound. This then shows us the types of elements or atoms present in the compound as well as the ratio of different atoms present. Examples include:
-
Sodium chloride - NaCl (for compounds that contain both metallic and non-metallic elements, the symbol of the metallic element is always written first)
-
Water - H2O (the number of atoms within elements is always written as a subscript; this is only applicable for atoms higher than 1)
-
Carbon dioxide – CO2 (oxygen atoms are usually written at the very end)
-
Magnesium oxide – MgO (it is best to reduce the subscript to the lowest term, e.g., in this case, it is MgO and not Mg2O2)
Mixture
What is a Mixture?
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which each substance retains its chemical substances. This means that they are not chemically combined. A mixture can be broken down with the help of physical separation techniques such as filtration, simple distillation and sublimation.
Mixtures can be made up of both elements and compounds. Its composition need not be fixed i.e. they can present in any ratio.
Mixtures can be found in the following forms:
-
Two elements, e.g. helium (He) and oxygen (O2)
-
Two compounds, for e.g. water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2)
-
An element and a compound, e.g. oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2)
Key Differences Between a Compound and a Mixture
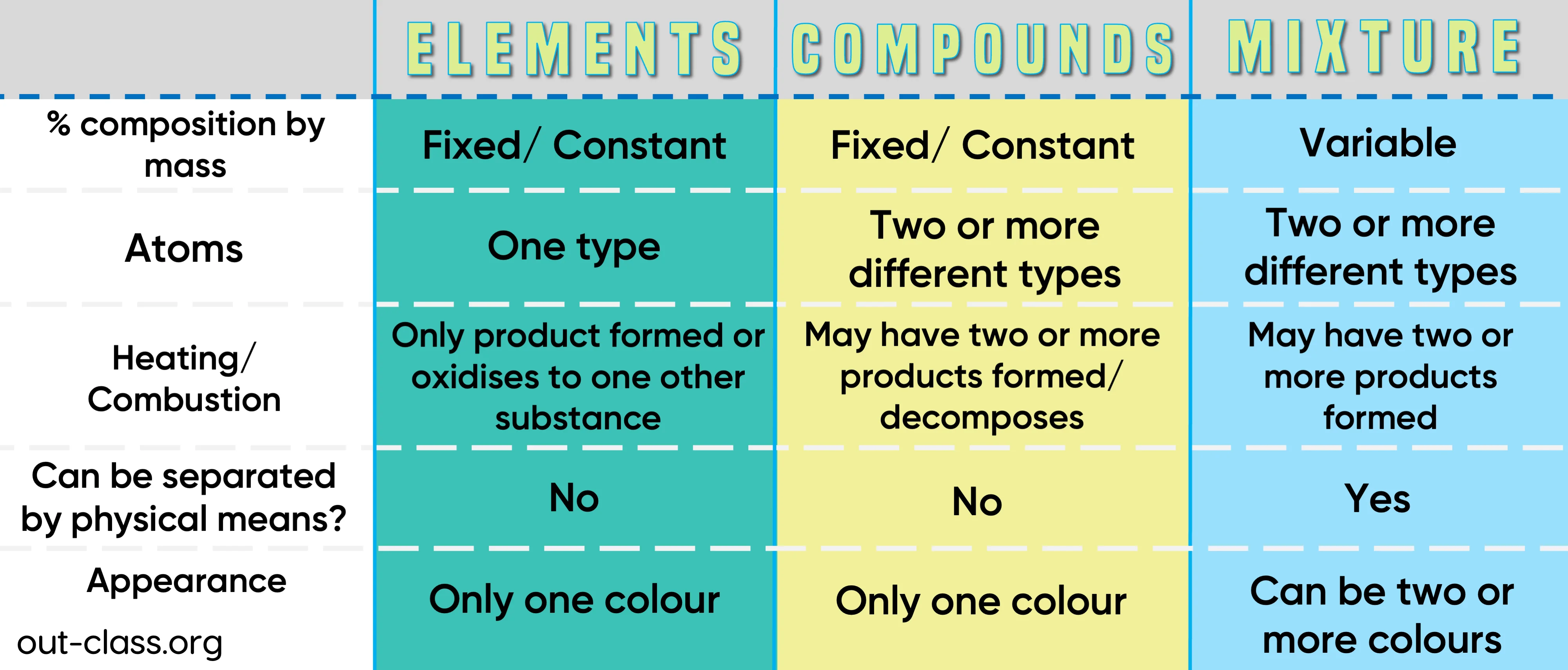
There are four main differences between a compound and a mixture. These can be examined in terms of:
Separation
Compounds can be broken down into simpler compounds whereas mixtures can be separated by physical processes.
Properties
The physical and chemical properties of a compound are different from that of its elements whereas the chemical properties of a mixture are the same as that of its components.
Energy changes
Energy changes such as heat/light energy are involved - a chemical reaction takes place when a compound is formed whereas there is no chemical reaction at the time a mixture is formed.
Composition
Number of elements within a compound is always in a fixed ratio whereas the components of a mixture can be in any ratio.
*Tip: The easiest way to remember this is by remembering the acronym SPEC.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures is what will help us understand the nature of matter.
FAQs
Q. What is an element in Chemistry?
An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom. It cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
Q. Can you give some examples of elements?
Sure, here are some examples of elements along with their chemical symbols: Calcium (Ca), Carbon (C), Chlorine (Cl), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Iron (Fe), Neon (Ne), Silicon (Si), Sodium (Na), and Germanium (Ge).
Q. What is a compound in Chemistry?
A compound is a substance made up of two or more different elements that are chemically combined in fixed proportions. It can be broken down into simpler substances through chemical processes.
Q. Can you provide examples of compounds and their chemical formulas?
Certainly, here are some examples of compounds along with their chemical formulas: Sodium chloride (NaCl), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Copper II sulfate (CuSO4), and Magnesium oxide (MgO).
Q. How are compounds represented in chemical formulas?
Compounds are represented in chemical formulas by combining the symbols of the elements that make up the compound. The subscripts indicate the ratio of different atoms present in the compound.
Q. What is a mixture in Chemistry?
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which each substance retains its chemical properties. It can be separated by physical processes and its composition is not fixed.
Q. What are some physical separation techniques used for mixtures?
Physical separation techniques for mixtures include filtration, simple distillation, sublimation, and others depending on the properties of the substances in the mixture.
Q. What are the main differences between compounds and mixtures?
The main differences include separation (compounds can be broken down into simpler compounds, mixtures can be separated by physical processes), properties (compounds have different properties from their elements, mixtures have properties similar to their components), energy changes (compounds involve energy changes during formation, mixtures do not), and composition (compounds have fixed ratios of elements, mixtures can have any ratio).
Q. How can I remember the differences between compounds and mixtures?
You can remember using the acronym SPEC: Separation, Properties, Energy changes, Composition.
Compounds have specific separation methods, different properties, energy changes during formation, and fixed compositions. Mixtures, on the other hand, have various separation methods, similar properties to components, no energy changes during formation, and variable compositions.
Q. Why is understanding the nature of elements, compounds, and mixtures important in Chemistry?
Understanding these concepts helps in analyzing and manipulating substances, predicting chemical behaviour, and designing experiments in various scientific fields. It forms the basis for studying reactions, properties, and interactions of matter.