Ah, the world of Cellular Biology — a terrain often filled with perplexity for IGCSE, O/A Level students and those braving entry tests. If you've ever found yourself scratching your head over the seemingly cryptic realms of intracellular and extracellular, fear not! Today, we're embarking on a journey to simplify these terms and shed some light on cellular life.
Let's start by acknowledging the elephant in the room: What do intracellular and extracellular even mean? It's a question that has echoed through many a classroom, leaving students in a state of bewilderment. But worry not; we're about to unravel the mysteries.
What is Intracellular?
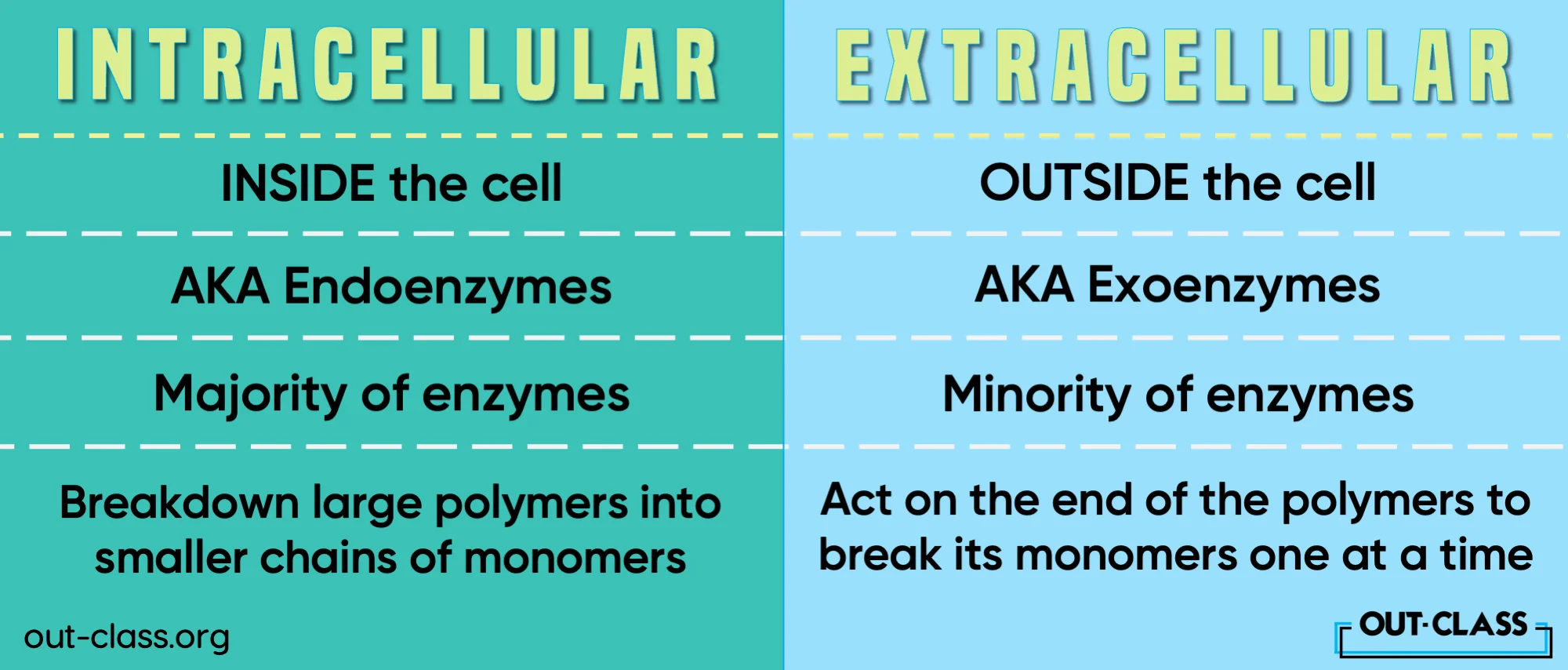
Intracellular refers to things “inside” a cell. So, when someone tosses around the term 'intracellular,' they're directing your attention to the inner workings, the backstage of cellular life.
What is Extracellular?
Extracellular refers to things “outside” a cell. It's where cells communicate, where signals are exchanged, and where the grand narrative of life unfolds.
Difference Between Intracellular and Extracellular Fluid
Intracellular fluid is found inside the cells and contains the following key components to name a few:
-
Ions (e.g. Mg2+, K+)
-
Various proteins
-
Amino acids, glucose
-
Nucleic acids
Extracellular fluid surrounds a cell from the outside. It may contain:
-
Oxygen molecules that must diffuse into the cell
-
CO2 molecules that exit as waste products from the cell
-
Other waste products like urea
-
Ions, vitamins, and nutrients
*Note: Intracellular and Extracellular fluid are separated by the plasma membrane (also referred to as the cell membrane). This membrane allows the selective transfer of molecules across it.
Extracellular vs. Intracellular Enzymes
Enzymes help speed up biochemical reactions in the body. Some (intracellular enzymes) assist chemical pathways inside the cell, whereas others help in chemical reactions outside the cells. Both can have specific temperature and pH requirements for proper functioning.
Intracellular Enzymes Examples
-
DNA Polymerase assists in DNA replication
Extracellular Enzymes Examples
-
Amylase in saliva breaks down food
-
Pepsin in the stomach helps digest proteins
-
Lipase secreted by the pancreas breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol in the intestine
Conclusion
Understanding intracellular and extracellular differences is crucial for O/A Level Biology and entry test students. Intracellular and extracellular environments largely differ in terms of the fluid they contain and the enzymatic actions taking place.
FAQs
Q. What does "intracellular" mean in cellular biology?
Intracellular refers to things inside a cell, focusing on the internal processes and components within the cellular structure.
Q. How is "extracellular" defined in cellular biology?
Extracellular pertains to things outside a cell, where external communication, signalling, and exchanges occur.
Q. What is the significance of understanding intracellular and extracellular environments?
Understanding these environments is crucial for grasping cellular processes, communication, and the overall functioning of living organisms.
Q. How are intracellular and extracellular fluids different?
Intracellular fluid is found inside cells and contains ions, proteins, amino acids, etc. Extracellular fluid surrounds cells and may contain oxygen, CO2, waste products, ions, vitamins, and nutrients.
Q. What separates intracellular and extracellular fluids?
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, separates intracellular and extracellular fluids, allowing selective transfer of molecules.
Q. Do intracellular and extracellular enzymes have specific functions?
Yes, intracellular enzymes typically function within cellular processes, while extracellular enzymes are involved in chemical reactions outside cells.
Q. Where can students find additional resources to deepen their understanding of Cellular Biology?
Online educational platforms, textbooks, and resources like Out-Class provide in-depth materials and tutorials for a thorough exploration of cellular O Level and IGCSE Biology concepts.