Have you ever wondered why speed and velocity seem like the Cain and Abel of the Physics world, with one being the older, established sibling, while the other is the crafty younger one, always trying to find a shortcut? Let's dig into the difference between speed and velocity.
What is Speed?
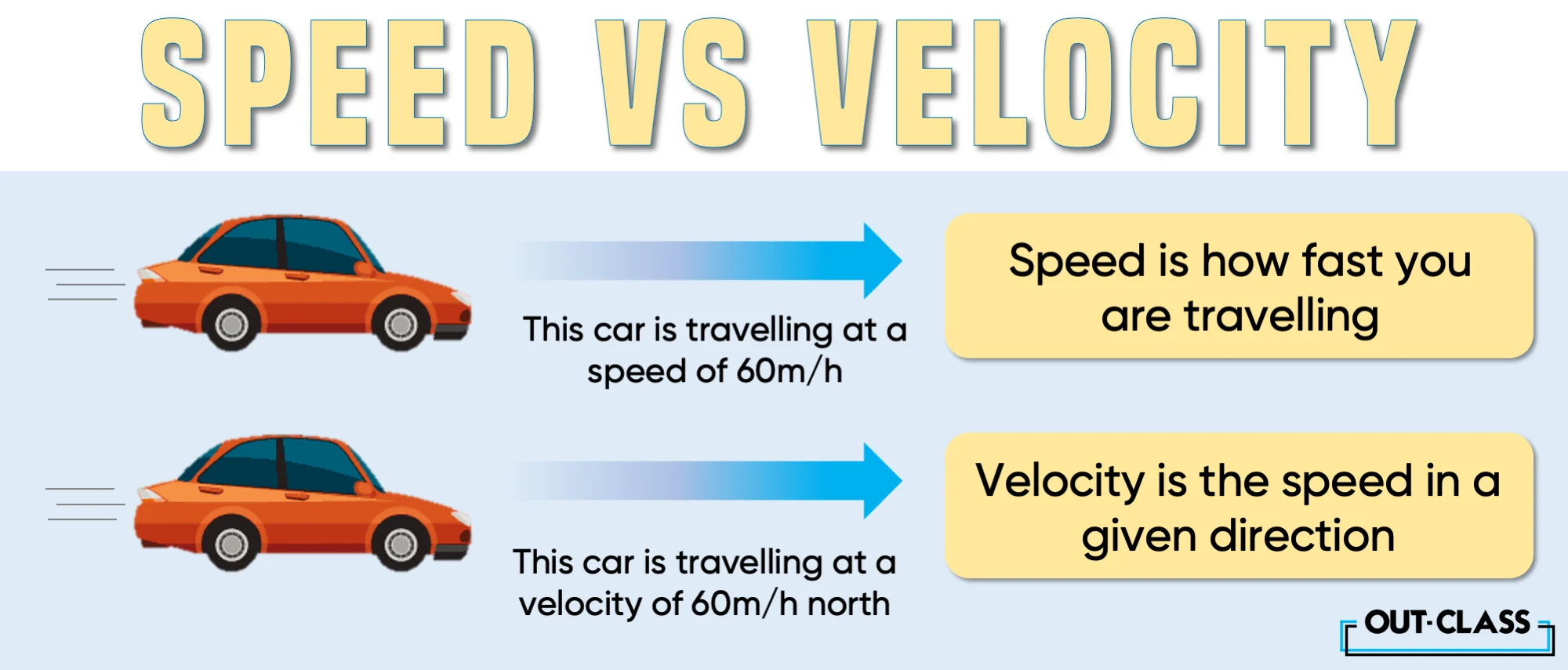
Speed, the seasoned older sibling, is the grandmaster of motion measurement. It tells us how fast an object is cruising from one point to another.
How to calculate Speed?
To calculate speed, use the trusty formula: Speed = Distance / Time. 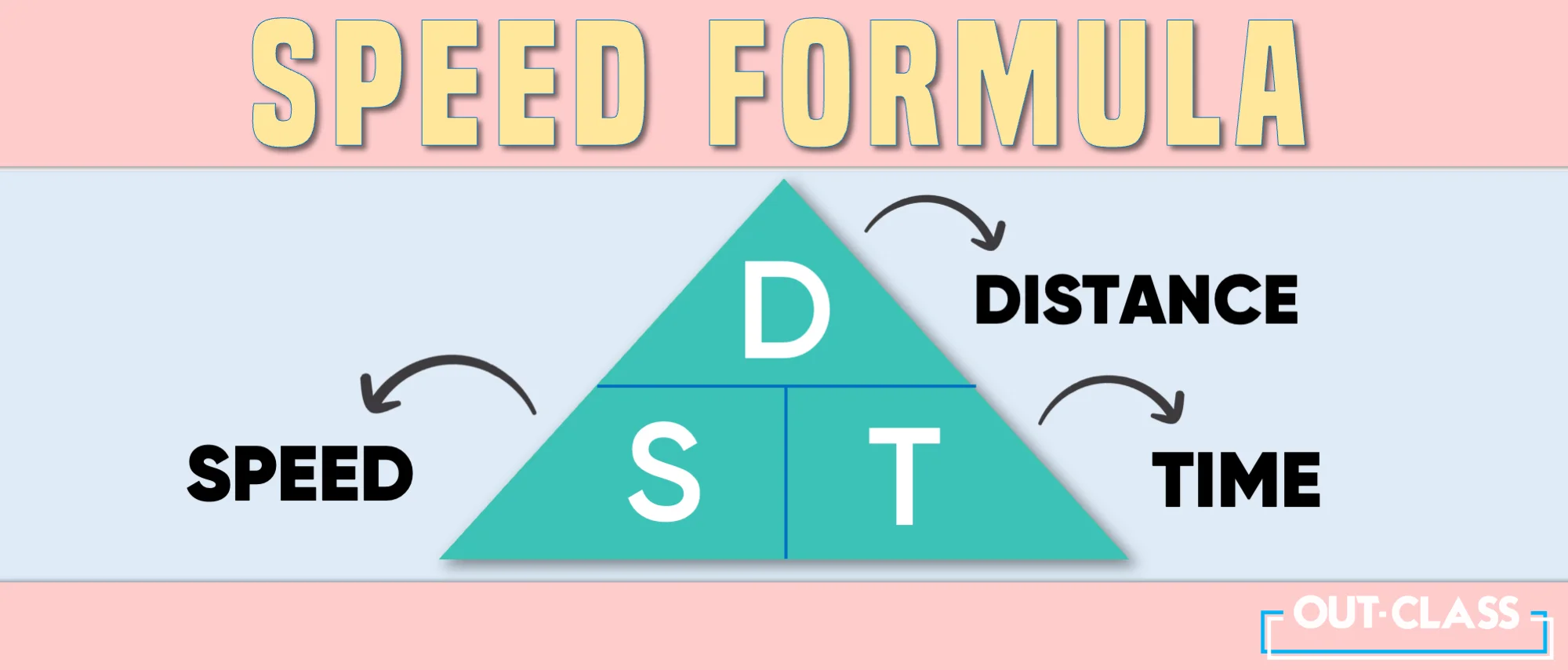
It's a scalar quantity and couldn't care less about direction – it's the no-nonsense member of the family. You could say it's the 'OG' of motion metrics.
What is Velocity?
Now, meet velocity, the younger sibling with an insatiable curiosity for shortcuts. Unlike speed, velocity is a vector quantity, giving us both the magnitude and direction.
How to calculate Velocity?
The formula for velocity is Velocity = Displacement / Time
It tells you how fast you're moving and where you're headed. It's like the tech-savvy GPS, always seeking those clever bypasses to beat traffic.
Types of Velocity
Now, let's remember the various types of velocity. This includes:
- Constant Velocity: when both speed and direction remain unaltered.
- Variable Velocity: when speed or direction changes along the way. It's like velocity is that younger sibling who's never content with the same old routine.
Example of Velocity
Imagine a car driving at 60 mph due north. That's velocity. But suppose the car suddenly takes a shortcut and heads northwest while maintaining a speed of 60 mph. In that case, the velocity changes – even though the speed remains the same. It's a prime example of velocity's craftiness.
Sibling Rivalry: The Inside Scoop
The rivalry between speed and velocity is less fierce than you might think. They work together like a dynamic duo. You can calculate the average speed formula by temporarily ignoring direction – to keep the peace in the family.
Conclusion
In summary, speed and velocity, while occasionally at odds, are two indispensable players in the IGCSE or O Level Physics game. What is speed but the steady, older sibling who keeps things simple, and what is velocity but the wily, younger one who's always looking for a quicker way to reach the destination? Understanding the difference between speed and velocity can help you navigate the fascinating world of Motion and Physics.
Most Commonly Repeated Questions:
Unlock the secrets to acing your O Level exams with a sneak peek into the most frequently asked questions that have graced the pages of O Level past papers!
- State how velocity differs from speed [1] [Oct/Nov 2020]
FAQs:
Q. What is the main difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures how fast an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction.
Q. How is speed calculated?
The formula for speed is Speed = Distance / Time.
Q. What is the formula for calculating velocity?
The formula for velocity is Velocity = Displacement / Time.
Q. Can velocity be negative?
Yes, velocity can be negative, indicating motion in the opposite direction. Positive velocity indicates motion in the chosen direction.
Q. Are speed and velocity always equal?
No, speed and velocity can be equal only when motion is in a straight line without changing direction.
Q. Can an object have constant speed but changing velocity?
Yes, if an object changes its direction while maintaining a constant speed, its velocity changes.
Q. What is constant velocity?
Constant velocity occurs when both the speed and direction of an object remain unchanged over time.