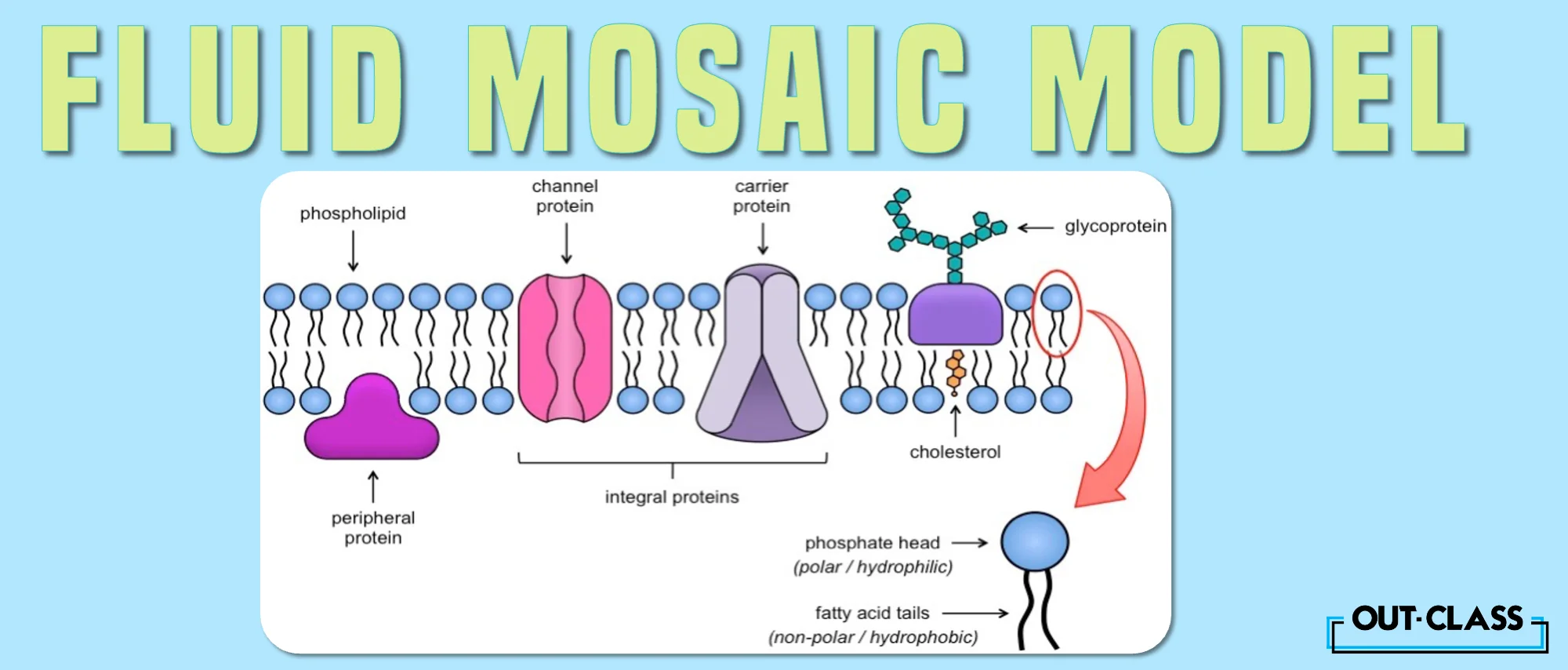
As a Biology student, you’ve surely come across the term “fluid mosaic model” when studying cells. But what is it and why is it called the fluid mosaic model? We answer these and other common questions below.
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model?
The fluid mosaic model of cell membranes describes it as a “collage” or “mosaic” of different chemical components.
Which components are features of the Fluid-Mosaic membrane?
The following are the components that are features of the fluid mosaic membrane:
-
Phospholipids
-
Cholesterol
-
Proteins
-
Carbohydrates
The fluid mosaic model is composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules (called the phospholipid bilayer). The hydrophobic (water “hating”) ends of both layers point inwards, whereas the hydrophilic (water “loving”) ends meet the water medium inside and outside of the cell.
Why are Cell Membranes called Fluid Mosaics?
Imagine that the fluid mosaic membranes contain a sea of phospholipids with proteins and carbohydrate molecules floating around like boats. Together, these form a tapestry (mosaic) of components that appear dynamic and flexible (fluid).
Why is the Fluid Mosaic Model Important?
Cell membranes are fluid mosaics and this grants them varied functionality:
-
The complex network of carrier proteins and phospholipid bilayer allows selected entry of molecules.
-
This helps maintain the correct potential gradient inside the cell.
-
Moreover, it ensures the availability of useful molecules for cellular processes.
-
Linkage of phospholipids with cholesterol helps keep the membrane elastic and intact.
Conclusion
The next time you ponder, “Are fluid mosaic cell membranes?”, you’ll know the answer! The fluid mosaic model captures the intricate structure of cell membranes and their functioning as selectively permeable dividers.
FAQs
Q. What is the Fluid Mosaic Model?
The fluid mosaic model of cell membranes describes them as a dynamic and flexible "collage" or "mosaic" of different chemical components, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Q. Which components are features of the Fluid Mosaic membrane?
The components featured in the fluid mosaic membrane include phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. These elements create a dynamic structure known as the phospholipid bilayer.
Q. Why are Cell Membranes called Fluid Mosaics?
Cell membranes are called fluid mosaics because they consist of a dynamic and flexible arrangement of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. This fluidity allows for selective permeability and maintains the integrity of the membrane.
Q. Why is the Fluid Mosaic Model Important?
The fluid mosaic model is important as it explains the dynamic nature of cell membranes, allowing selective permeability for the entry and exit of molecules. It also highlights the role of different components in maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of cell membranes.