Introduction to Photosynthesis
Ready to ace your biology exams and gain a deeper understanding of one of life's most essential processes? Photosynthesis isn't just a pivotal concept in the Biology curriculum—it's a frequent topic in the CAIE exams, particularly for O Levels and IGCSEs. This guide is designed to help you master the Photosynthesis equation, grasp its definition, and tackle commonly repeated past paper questions. Dive right in to discover how plants convert sunlight into energy and why this process is vital for all life on Earth. Get ready to boost your grades and your knowledge with this comprehensive study resource!
What is Photosynthesis?
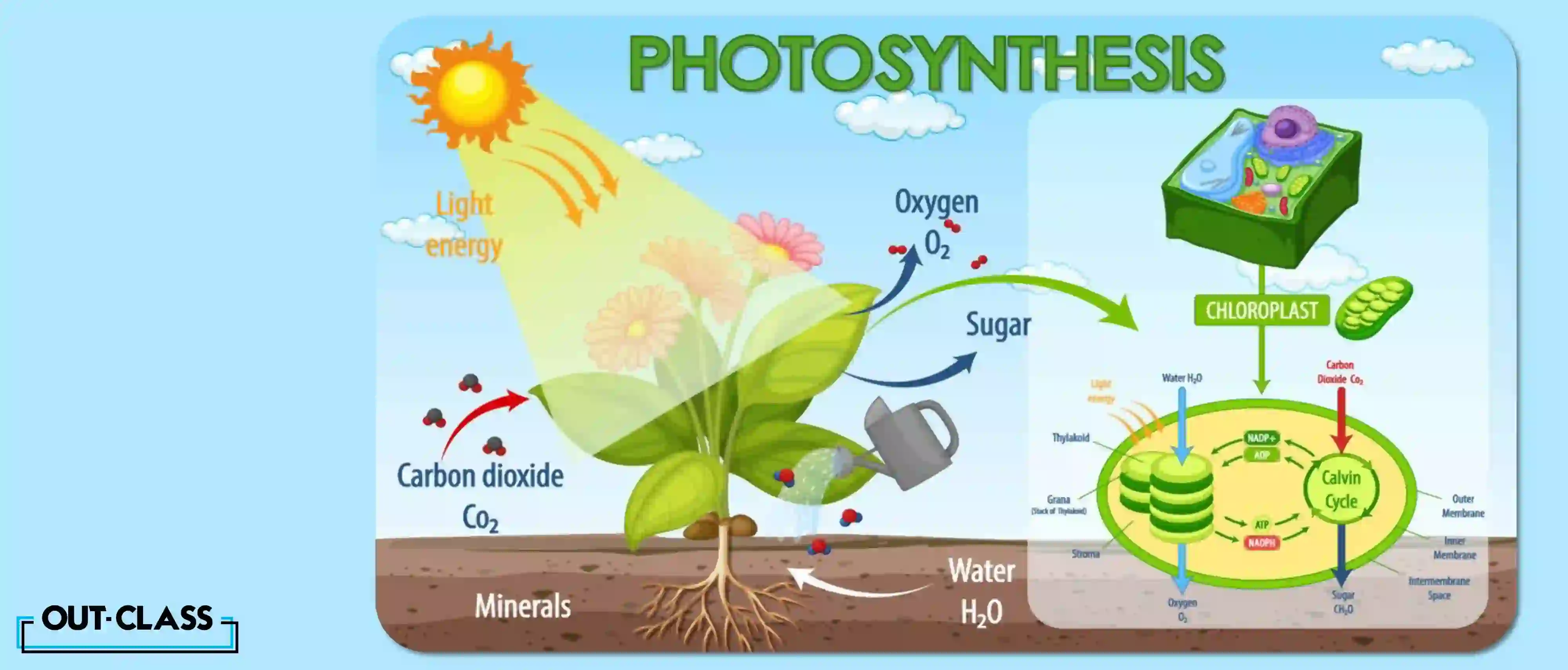
It’s the process by which cellular organisms, like green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy to propel their biological activities. In simpler terms, it is the process in which green plants, algae and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make their own food. Herbivores obtain energy by eating these plants and in turn, carnivores eat the herbivores. As a foundational part of the food chain, almost all living organisms rely on photosynthesis.
Understanding the Photosynthesis Equation:
Photosynthesis equation:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
6 (Carbon Dioxide + Water) + Light Energy -> 6 (Glucose + Oxygen)
This photosynthesis equation encapsulates the magical conversion of sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen – a fundamental concept for O Level and IGCSE Biology students.
Decoding the Photosynthesis Process:
Photosynthesis is nature’s magic show, hosted within the chloroplast.
The process begins with water entering the roots of a plant and travelling to the leaves. Carbon dioxide enters the plant through the stomata. Stomata are tiny pores through which plants breathe. They are found on the top and underside of leaves, stems, roots and flower petals.
The chloroplast processes plants and synthesises carbohydrates from raw materials by harnessing light energy. The chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll that captures light energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy. This process initiates the synthesis of glucose and releases oxygen as a by-product.
The plant, then, uses glucose as a chemical energy to help the plant grow. Glusocse also provides chemical energy to organisms that may consume the plant.
Read more: Photosynthesis vs. Respiration
Mastering IGCSE and O Level Past Paper Questions on Photosynthesis:
Solidify your knowledge by tackling IGCSE & O Level past paper questions on Photosynthesis. This section offers a practical approach to reinforce learning, allowing students to gauge their understanding and readiness for O Level & IGCSE exams.
Most Common Repeated Questions:
-
- Which row shows what happens in photosynthesis?
A. Chemical energy to light energy -> glucose -> starch
B. Chemical energy to light energy -> starch -> glucose
C. Light energy to Chemical energy -> glucose -> starch
D. Light energy to Chemical energy -> starch -> glucose - Which factor is limiting the rate of photosynthesis at point X?
A. Availability of chlorophyll
B. Availability of water
C. Concentration of carbon dioxide
D. Intensity of light - A young plant may wilt when dug up and re-planted in another place. What causes this?
A. Leaves lose less water
B. Roots cannot take up mineral salts
C. Stem cannot transport water
D. Surface area of the root is reduced
- Which row shows what happens in photosynthesis?
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is the cornerstone of plant biology, demanding meticulous attention in O Level and IGCSE. With a profound understanding of the equation, definition, keynotes, and honed skills from IGCSE and O Level questions on Photosynthesis, students can confidently navigate Photosynthesis IGCSE and O Level Biology.
Learn more about Photosynthesis and its limiting factors as explained in graphs.