In the intricate dance of O Level Economics, demand and supply curves act as choreographers, responding to myriad factors that cause shifts and movements. Let's delve into the dynamic world of economic forces, exploring what makes these curves sway and alter their course.
Understanding Shifts and Movements in Demand and Supply Curves
Shift in Demand and Supply Curves:
Shifts in demand and supply curves occur when external factors influence the entire demand or supply at all price levels. A variety of elements causes these shifts, and understanding them is crucial for predicting market dynamics.
Simultaneous Shift in Demand and Supply:
In the complex economic ballet, demand and supply curves sometimes pirouette simultaneously. This intricate dance reflects the interconnected nature of market forces, where changes in one curve trigger responses in the other, influencing the delicate balance of market equilibrium.
What Drives Movements and Shifts in Supply and Demand Curve?
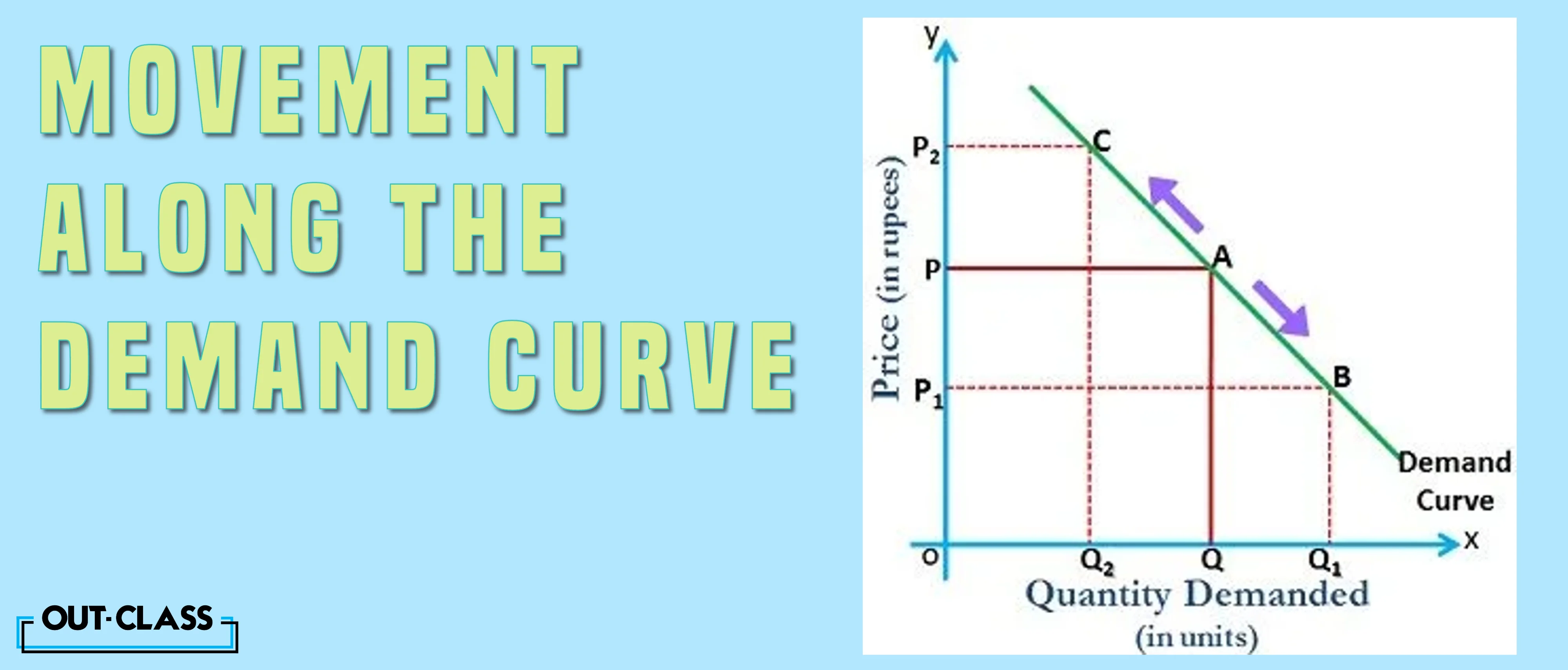
Movement Along Demand and Supply Curves:
Movements along the curves, on the other hand, are driven solely by changes in price. Price fluctuations prompt consumers and producers to adjust their behaviours, resulting in movements along the existing demand and supply curves.
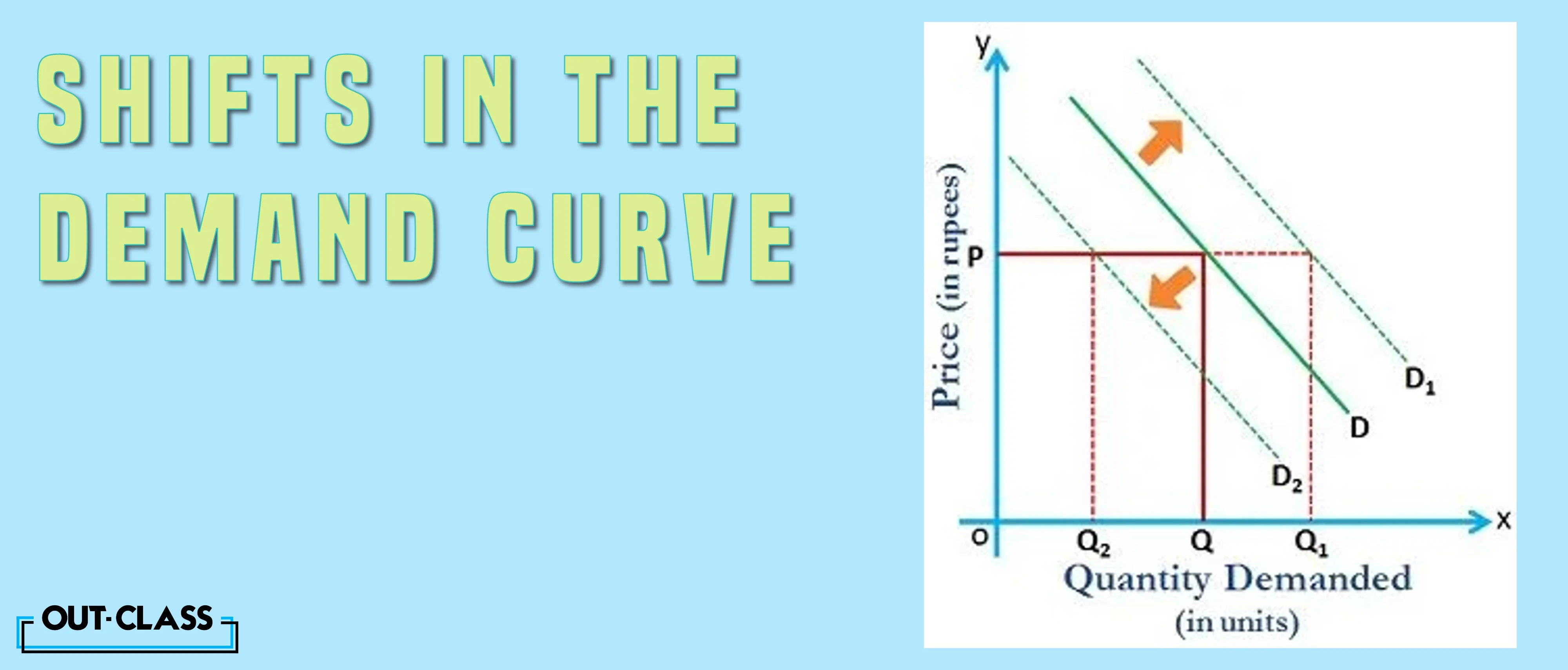
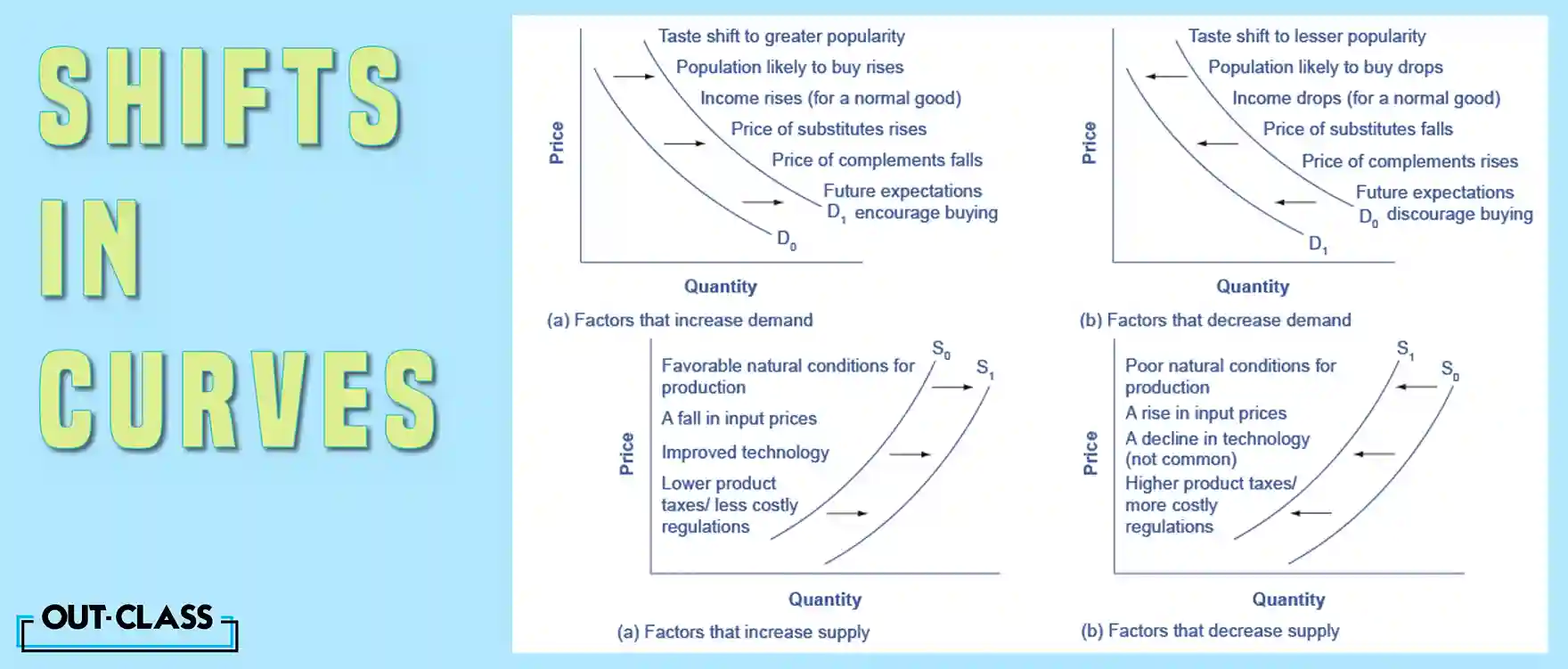
Factors Influencing Demand Curve Shifts:
Income, related goods, advertising, tastes and fashions, and expectations play pivotal roles in swaying the demand curve. An increase in demand means an outward shift, while a decrease in demand entails an inward shift of the demand curve.
Change in Income:
A rise in income correlates to increased demand for normal goods. For inferior goods, where a consumer's utility increases with less of this good, a rise in income decreases demand.
Change in Tastes and Preferences:
If preferences for good X increase, demand increases.
Change in Expectations:
Based on future price changes. If consumers expect the price of good X to increase, demand for it increases now.
Advertising:
This increases consumer loyalty to the good, resulting in increased demand.
Change in Price of Related Goods:
If the price of a substitute to good X increases, the latter's demand falls. Conversely, if the price of a complementary good increases, good X's demand decreases.
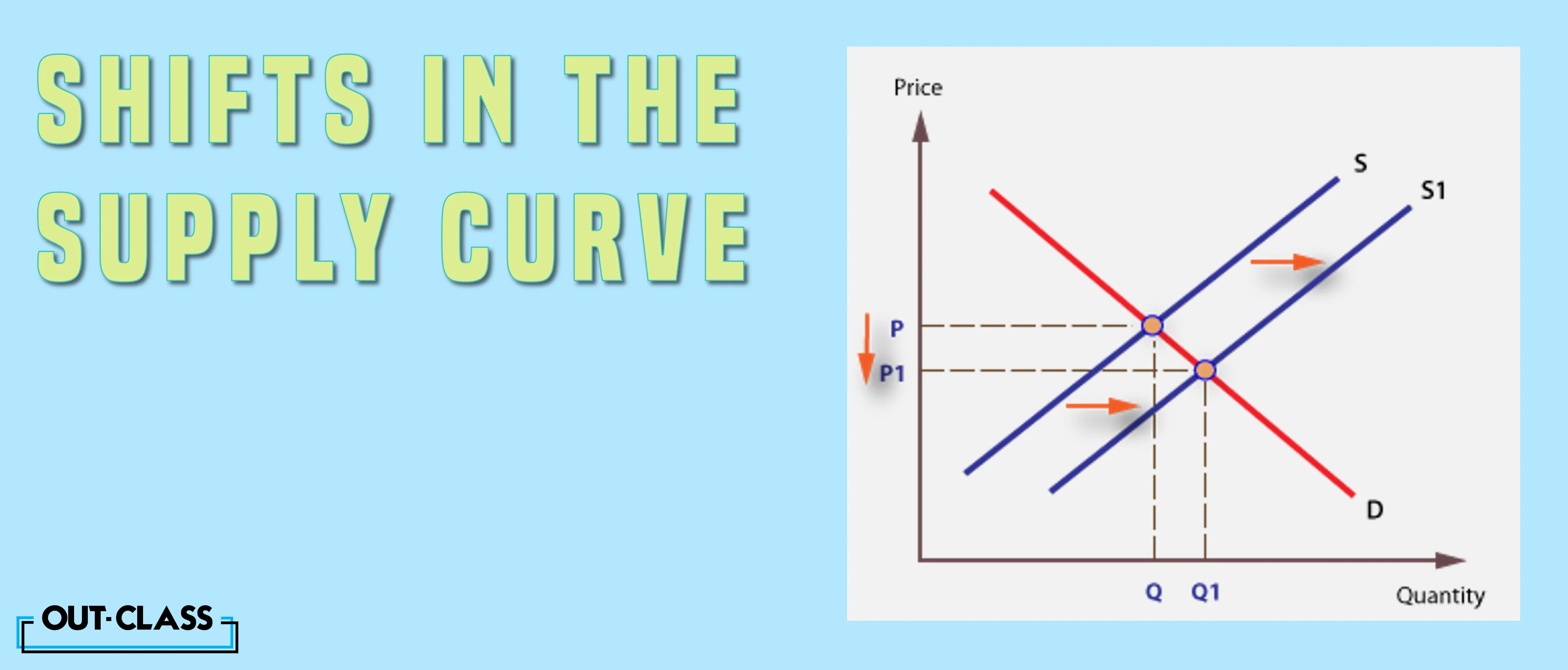
Factors Influencing Supply Curve Shifts:
Productivity, taxes, number of firms, technology, weather, and production costs are the driving forces that determine the supply curve's direction.
Production Costs:
If costs of production fall, the firm can afford to supply more. If costs rise, such as with higher wages, there will be an inward shift in supply.
Productivity:
Higher productivity causes an outward shift in supply as average costs for the firm fall.
Taxes & Subsidies:
Government policies can affect the cost of production and the supply curve through taxes, regulations, and subsidies. An increase in tax decreases supply and shifts the curve inward ( or towards the left) as the increase in tax results in higher costs. Government regulations that require firms to spend money to provide a cleaner environment or a safer workplace also increase costs, thus shifting the supply curve inward.
On the other hand, an increase in subsidies reduces the cost of production and increases supply at every given price, shifting supply to the right. It is because subsidies occur when the government pays a firm directly or reduces the firm’s taxes if the firm carries out certain actions.
Technology:
Advanced technology leads to more efficient production (firms produce at a lower cost), resulting in an outward shift in supply.
Number of Firms:
An increase in firms increases supply, shifting the curve to the right.
Weather:
Particularly relevant for agricultural produce. Favorable conditions, such as a good harvest, increase supply and thus, the supply curve would shift to the right. On the other hand, a drought decreases the supply of agricultural products, which means that at any given price, a lower quantity will be supplied.
Shifts in Demand and Supply Curve:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between demand and supply curves is a captivating spectacle. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone navigating the complex world of O Level Economics, whether it's the simultaneous shift influenced by multiple factors or the nuanced movements along the curves dictated by price changes.
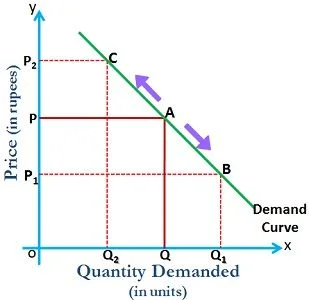
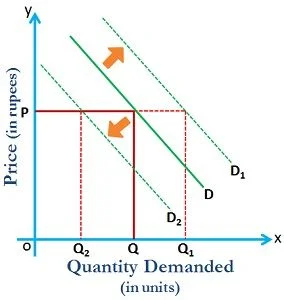
Key Differences Between Movement and A Shift in a Curve:
| Movement in the Curve | Shift in the Curve | |
| Meaning | Movement in the curve is when the commodity experience change in both the quantity demanded and price, causing the curve to move in a specific direction. | The shift in the curve is when the price of the commodity remains constant, but there is a change in quantity demanded due to some other factors, causing the curve to shift to a particular side. |
 |
 |
|
| What is it? | Change along the curve | Change in the position of the curve |
| Determinant | Price | Non-Price |
| Indicates | Change in Quantity Demanded or Supplied | Change in Demand/Supply |
| Result | Curve will move upward or downward | Curve will shift rightward or leftward |
What IGCSE and O Level Economics Crash Course Unveils: A Sneak Peek
- Focused Revision: No more drowning in a sea of information. The Out-Class O Level crash course hones in on the key topics, ensuring your revision is targeted and effective.
- Exam Strategies: Ace your IGCSE and O Level Economics exam with proven strategies that go beyond rote memorization. We equip you with the skills to tackle any CAIE question with finesse.
- Quick Mastery: Short on time? No problem! Our crash course is designed for swift yet thorough understanding, getting you up to speed in no time.
Here is a visual SNEAK PEEK into how this topic is taught:
FAQs:
Q. What causes shifts in demand and supply curves?
Shifts in demand and supply curves are caused by various external factors. For demand, factors include income changes, related goods, advertising, tastes, and expectations. For supply, factors include productivity, taxes, the number of firms, technology, weather, and production costs.
Q. What is the difference between a shift and a movement along the demand and supply curves?
A shift occurs when external factors influence the entire demand or supply at all price levels, leading to a change in the entire curve. A movement along the curves happens solely due to changes in price, affecting the quantity demanded or supplied at a specific price level.
Q. How does a change in income influence demand?
A rise in income usually leads to increased demand for normal goods. For inferior goods, where utility increases with less consumption, a rise in income might decrease demand.
Q. What factors influence the supply curve?
Factors influencing the supply curve include production costs, productivity, taxes, technology, the number of firms, and weather conditions. Changes in these factors can lead to shifts in the supply curve.
Q. How does advertising impact demand?
Advertising can increase consumer loyalty to a product, resulting in an increase in demand. This is one of the factors that can cause a shift in the demand curve.
Q. How does a change in technology affect the supply curve?
Advanced technology leads to more efficient production, which can result in an outward shift in the supply curve. This means that firms can supply more at every price level.
Q. What happens to supply when there is an increase in taxes?
An increase in taxes typically decreases supply, leading to an inward shift in the supply curve. This is because higher taxes increase the cost of production for firms.
Q. How does a change in weather affect the supply of goods?
Weather conditions, especially relevant for agricultural produce, can impact supply. Favorable conditions, such as a good harvest, can increase supply, while adverse weather conditions may decrease it.