Everything You Need to Know about the Functions of a Spectrophotometer.
Have you ever wondered how scientists can measure the colour of a substance or how much light it absorbs? It’s fine if you didn’t. Well, they use a special instrument called a spectrophotometer. And that is the function of a spectrophotometer.
Simply put, a spectrophotometer is a device that measures the amount of light that passes through or is reflected by a sample. By doing this, it can tell us information about the chemical composition, concentration, and structure of the sample.
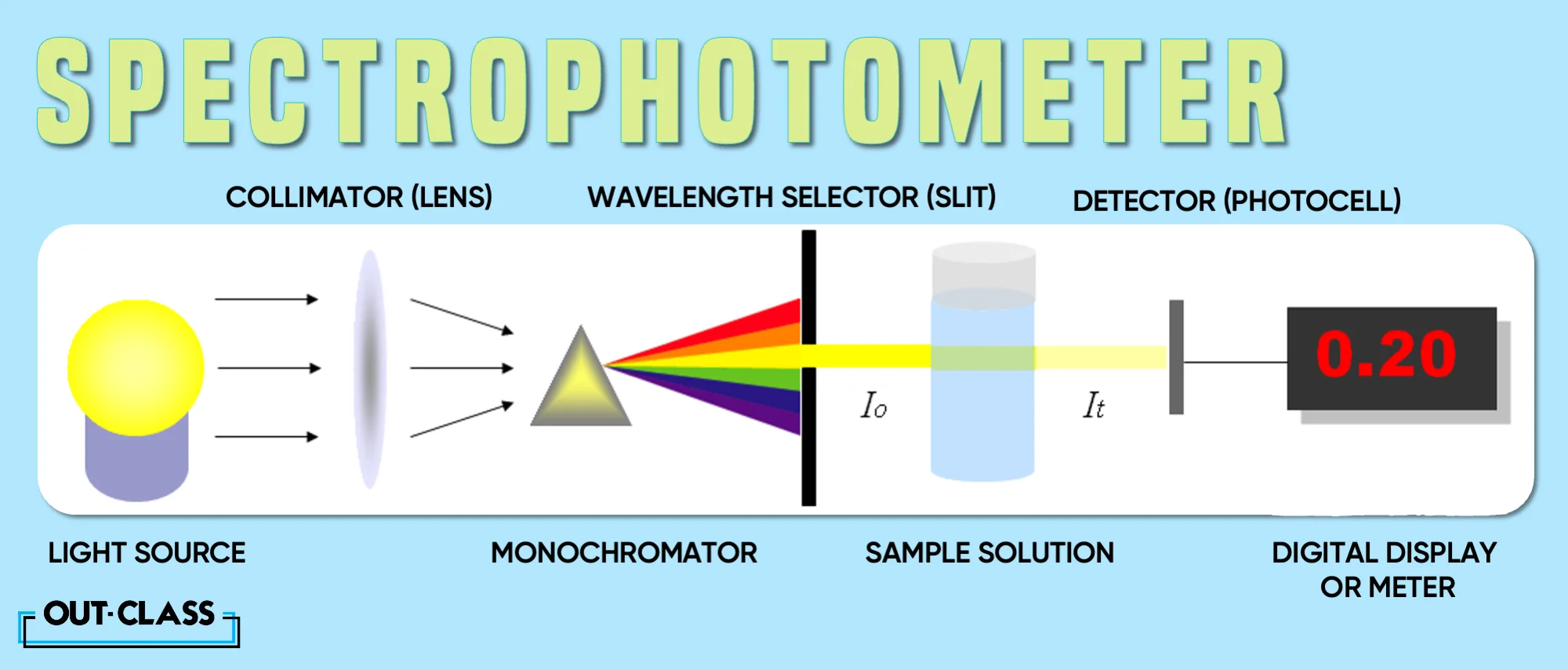
To not get too technical, a spectrophotometer simply works by shining a beam of light onto the sample and then measuring how much of that light is reflected.
-
Shining a beam.
-
Measuring its reflection.
To add to that, the light that reaches the sample can have different wavelengths, which correspond to different colours. For example, red light has a longer wavelength than blue light. And so, the sample can absorb some wavelengths more than others, depending on its properties.
This creates a unique pattern of light absorption, called a spectrum. A spectrum is what can be used to identify the sample of light or quantify its amount.
Five Fundamental Components of a Spectrophotometer:
The five fundamental components of a spectrophotometer are:
-
A light source: This is just like a flashlight that shines light on the sample. The light can be of various types, depending on what you want to measure. Some light sources give out all colours of light, such as the sun. Others give out only specific colours, such as a laser pointer.
-
A monochromator: This a filter that splits the light into different colours, simple. It can either be a prism or a grating. A prism is a glass triangle that makes a rainbow when light passes through it. A grating is a comb with very fine teeth that makes a spectrum when light passes through it. This is a very unique function of a spectrophotometer.
-
A sample holder: As worded, this is where you put the sample for measurement. The sample holder can be either a cuvette or a reflectance probe. A cuvette is like a small glass box that holds liquid or solid samples. A reflectance probe is like a stick that touches the surface of solid or opaque samples.
-
A detector: Also known as a sensor which measures how much light passes through or is reflected by the sample, a very important purpose of a spectrophotometer. The detector can be either a photodiode or a photomultiplier tube, hold on we’ll explain:
A photodiode is like a battery that produces an electric current when light hits it.
A photomultiplier tube is like an amplifier that makes the electric current bigger when light hits it.
Again, a very crucial element of the five fundamental components of a spectrophotometer -
A readout device: This is where you see the results of the measurement, reading it out. It can be either an analogue meter or a digital display. Without this, the function of a spectrophotometer goes un-understood. An analogue meter is a gauge that shows the intensity of light as a needle on a scale. A digital display is like a screen that shows the intensity of light as a number or a graph.
Types of spectrophotometry:
Let's delve into the types of spectrophotometry.
To reiterate, the function of a spectrophotometer is to measure how light interacts with a sample.
Now, the types of spectrophotometry are:
-
UV-visible spectrophotometry: It uses light in the UV and VIS range (185 - 700 nm). It measures how molecules with chromophores (parts that absorb light) affect the light. This allows it to trace the amount of substances like proteins, DNA, and drugs in solutions.
-
IR spectrophotometry: It uses light in the IR range (700 - 15000 nm). It determines how molecules with vibrational modes (movements of atoms) affect the light. It can identify functional groups like alcohols and carboxylic acids in organic compounds.
-
Fluorescence spectrophotometry: It uses light in any range of wavelengths. It measures how molecules with fluorescence (the ability to emit light) simply affect the light. It can detect very minute amounts of substances like pollutants, pesticides, and biomarkers in samples.
What even is the purpose of spectrophotometry?
To be fair, the purpose of spectrophotometry is very diverse. It ranges from collecting quantitative and qualitative information about samples based on their interaction with light. Spectrophotometry is also widely used in various fields such as Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Medicine, Engineering, and Environmental Science. So, it is an essential tool for research and analysis in many applications which help you live. You asked what the function of a spectrophotometer is, well it is to discover drugs, clinical diagnosis, food quality control or to determine how much pollution is where.
Conclusion
Spectrophotometry is a method of studying how different substances react with light. It can help us find out the colour, amount, and type of substances in a sample. A spectrophotometer is a device that uses light to do this. It has five main parts: a light source, a device that splits the light into different colours, a place to put the sample, a device that measures the light that passes through or bounces off the sample, and a device that shows the results.
Different kinds of spectrophotometry use different kinds of light, such as ultraviolet, infrared, or fluorescent light. These methods can help us study different things, such as proteins, DNA, organic compounds, pollutants, and biomarkers.
We hope this study guide was beneficial for you!