You've studied how plants absorb water. But have you ever wondered how they release it? Dive into this article to unravel the secret and ace your IGCSE and O Level Biology course.
What is Transpiration in Plants
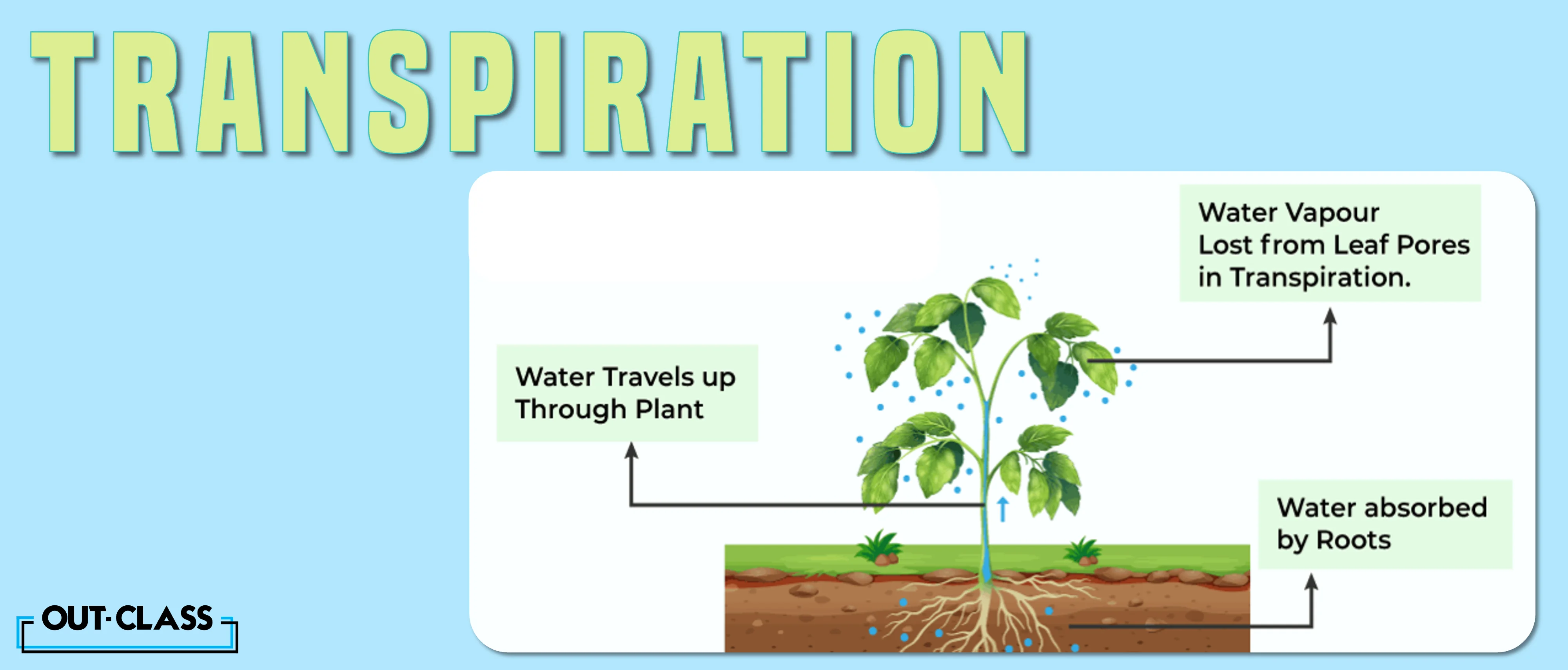
It is a process through which plants release water vapour to their surroundings. IGCSE and O Level Biology students often have the question, “Transpiration in plants occurs through what exactly?”
The answer is stomata. Stomata are tiny openings, often found on the underside of leaves. They allow water from inside the leaf to escape to the surroundings. This “diffusion” of water vapour occurs down the concentration gradient.
If you are not comfortable with the concepts of diffusion and concentration gradient, read our article here for a complete explanation!
Importance of Transpiration in Plants
A plant doesn’t just release water without reason. This process serves vital purposes:
-
Release of water helps cool the plant, just like how sweating helps reduce human body temperature
-
It also helps the plant turgid and upright
Factors Affecting Transpiration in Plants
Factors affecting transpiration in plants are:
Light
Stomata opens wider in bright light, increasing the rate of transpiration.
Humidity
High humidity reduces transpiration. If there is already moisture in the outside air, water vapour won’t diffuse out of the stomata as easily.
Wind
Faster wind carries away the released water vapour, setting up a steep concentration gradient and increasing transpiration.
Tips to Ace Transpiration Questions in IGCSE/O Level Biology
We are often asked: “Is IGCSE/O Level Biology hard?”. Not at all, if you take time building concepts:
-
Memorize the factors that affect the rate of transpiration in plants and understand their explanations.
-
Jot down bullet points on the importance of transpiration in plants
Conclusion
To recap, the meaning of transpiration in plants is “breathing out” water vapour. Transpiration is useful for plants because it aids cooling and helps maintain turgidity.
Remember, being thorough with this chapter can help you score top marks in IGCSE/O Level Biology. If you found this guide useful and want to learn more, stay tuned to Out-Class for more!
Most Common Repeated Questions:
Unlock the secrets to acing your IGCSE and O Level exams with a sneak peek into the most frequently asked questions that have graced the past papers!
-
Outline the movement of water through a leaf during the process of transpiration. (5)
-
Leaves from different plant species transpire at different rates in the same environmental conditions. Suggest and explain structural differences in the lower surface of these leaves which might produce differences in the transpiration rate (3) [Oct/Nov 2022]
FAQs:
Q. What is transpiration in plants?
Transpiration in plants is a process through which they release water vapour to their surroundings. It primarily occurs through tiny openings called stomata, typically found on the underside of leaves. Transpiration helps cool the plant and maintain turgidity.
Related: Photosynthesis vs Respiration
Q. How does transpiration occur in plants?
Transpiration occurs through stomata, which are small openings on the surface of leaves. Water from inside the leaf evaporates and diffuses out through stomatal pores. This process is driven by the concentration gradient, with water vapour moving from areas of higher concentration inside the leaf to lower concentration in the surrounding air.
Q. What factors affect the rate of transpiration in plants?
Several factors influence the rate of transpiration in plants:
Light: Stomata open wider in bright light, increasing the rate of transpiration.
Humidity: High humidity reduces transpiration as water vapour diffusion is less effective in moist air.
Wind: Faster wind carries away water vapour, setting up a steeper concentration gradient and increasing transpiration.
Q. Where can I find more resources for IGCSE/O Level Biology preparation?
For additional resources and comprehensive IGCSE or O Level Biology preparation, students can explore online platforms, textbooks, and educational websites. Out-Class offers courses and resources to aid in IGCSE/O Level Biology preparation.