Unveiling Zener Breakdown: A Key to Understanding Voltage Regulation.
Have you ever wondered how electronic devices maintain a stable and reliable power supply with fluctuating voltage? Just kidding, none of us have.
What even is reliable power? Is there no load shedding?
Well, for the sake of your O Level exam, we aren’t left with much of a choice. We must.
This is just delving into the science of Zener Breakdown, demystifying the magic that keeps our devices running smoothly.
What is a Zener Breakdown?
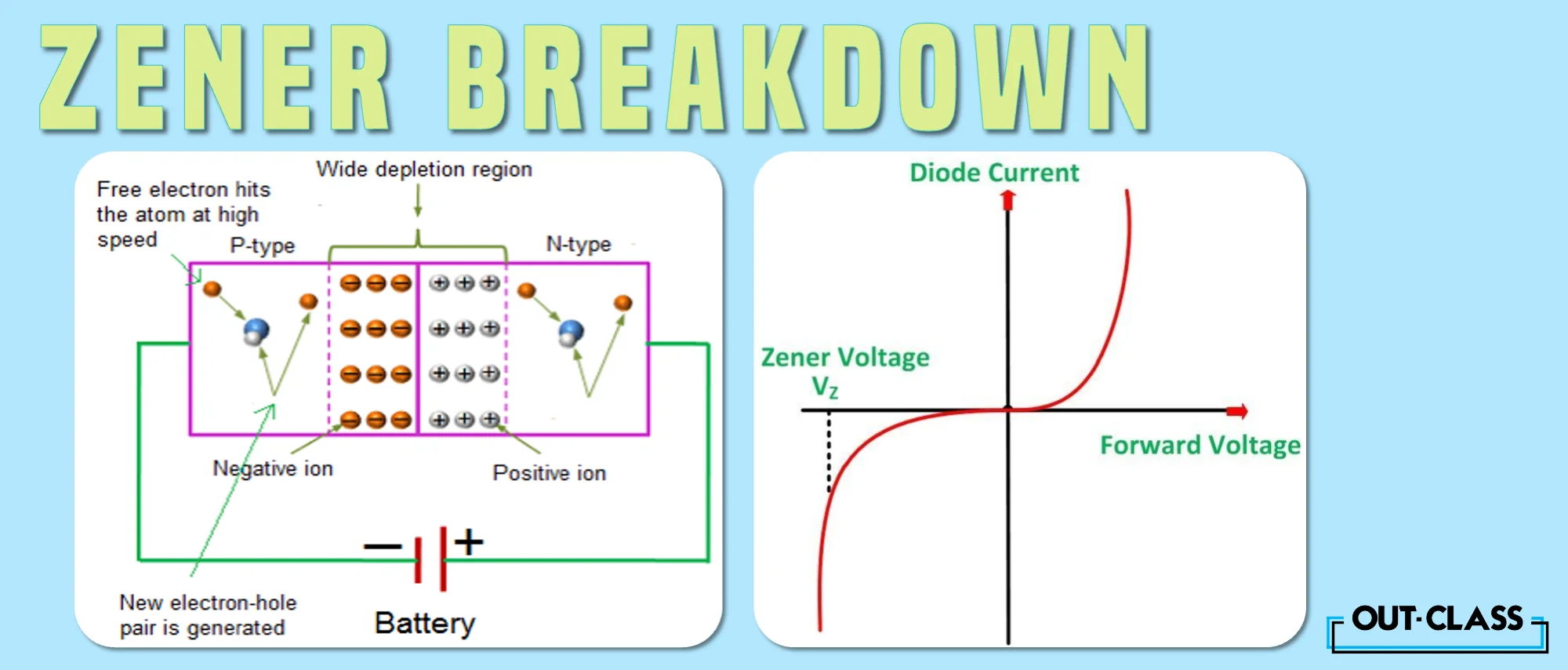
First things first, let’s define Zener diodes and Zener breakdown. Zener breakdown is a type of electrical breakdown. It occurs in a reverse-biased p-n diode when the electric field enables the tunnelling of electrons from the valence to the conduction band of a semiconductor, which leads to a sudden increase in the reverse current. Zener diode is a unique variety of p-n diodes created specifically for use in the reverse breakdown zone, we’ll explain it more below.
That’s too much science. Let us explain further. A p-n diode is a device that allows current to flow in one direction only. It is made of two types of semiconductor materials.
-
The p-type material has more holes (positive charge carriers) than electrons.
-
The n-type material has more electrons (negative charge carriers) than holes.
When the p-type and n-type materials are joined together, they form a p-n junction with a depletion region, and here, there are no free charge carriers.
Depletion Range & What is a breakdown voltage?
The depletion region is a barrier that prevents the current from flowing in the opposite direction. However, this barrier can be broken, and it's current flows in the opposite direction if a sufficient voltage is provided across the p-n junction. The breakdown voltage is just the name given to this voltage.
Zener Diode:
A unique variety of p-n diodes created specifically for use in the reverse breakdown zone is known as a Zener diode. Due to the semiconductor materials' high doping, it has an extremely tiny depletion region. This indicates that its breakdown voltage is very low—usually less than 5 volts.
Zener Effect:
The mechanism that results in the Zener breakdown is the Zener effect. The electrons in the semiconductor's valence band have more kinetic energy when a strong electric field is applied over the thin depletion zone. Some electrons tunnel past the barrier to the conduction band, where they can travel around freely. The additional electron-hole pairs produced by collisions of these free electrons with other atoms also become available to travel. The reverse current is rapidly increased by this process, which creates a large number of charge carriers.
The uses of zener diodes are employed by electronics for a variety of purposes, such as voltage regulation, voltage reference, surge protection, and switching. No matter how much the input voltage or load current fluctuates, it can still produce a consistent and stable voltage output.
Summary:
Zener breakdown is a fascinating electrical phenomenon in which a reverse-biased p-n diode experiences a sudden surge in reverse current at a specific voltage threshold, the breakdown voltage. This behaviour is rooted in the diode's one-way current control.
The Zener diode, designed for reverse breakdown, has a low breakdown voltage (often under 5 volts) due to its small depletion region and heavy semiconductor material doping. This design ensures a stable voltage output, even with varying input voltages and load currents.
The Zener effect, involving energetic electrons tunnelling across the depletion region, generates additional charge carriers and rapidly raises the reverse current. This practical application of semiconductor physics finds use in voltage control, voltage reference, surge protection, and switching in electronics.
Zener breakdown provides a reliable solution for electronic circuit design, bridging the gap between semiconductor theory and real-world electronics.


